Auger electron spectroscopy facts for kids

Auger electron spectroscopy (say: OH-jer ee-LEK-tron spek-TROS-koh-pee), often called AES, is a special way to figure out what chemical elements are on the very top layer of an object. Think of it like a super-detective tool for surfaces!
Contents
What is Auger Electron Spectroscopy?
AES is a powerful scientific method. It helps scientists learn about the tiny atoms that make up the surface of materials. It can tell them what elements are there and how much of each element is present. This is very useful in many fields, like making computer chips or studying how metals rust.
How Does AES Work? The Auger Effect
AES works by using a special natural event called the Auger effect. This effect was discovered by a French scientist named Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Here's how it happens:
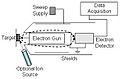
Step 1: Hitting the Sample
First, a machine shoots a beam of fast-moving electrons at the surface of the material you want to study. These electrons have a lot of energy.
Step 2: Knocking Out an Electron
When one of these fast electrons hits an atom on the surface, it can knock out another electron from deep inside that atom. This leaves an empty space, like a missing tooth.
Step 3: Filling the Gap
To fill this empty space, an electron from a higher energy level in the same atom quickly drops down into the gap. When this electron moves, it releases energy.
Step 4: The Auger Electron Appears
Instead of releasing this energy as light, the atom sometimes transfers it to another electron. This third electron then gets enough energy to escape from the atom completely. This escaping electron is called an Auger electron.
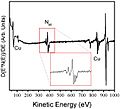
Reading the Signals
The energy of the Auger electron is unique. It's like a fingerprint for the atom it came from. AES machines measure the energy of these Auger electrons. By doing this, scientists can create a spectrum. This spectrum shows which elements are on the surface and how much of each there is.
What Can AES Tell Us?
AES is used for many things:
- Finding elements: It can identify almost all elements on the periodic table, except for hydrogen and helium.
- Surface cleanliness: It can check if a surface is clean or if there are tiny bits of dirt or other materials on it.
- Thin layers: It's great for studying very thin layers of material, like coatings on glass or metal.
- Chemical environment: Sometimes, it can even give clues about how atoms are connected to each other.
This makes AES a vital tool in science and technology. It helps us understand and create new materials.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Espectroscopia electrónica Auger para niños
In Spanish: Espectroscopia electrónica Auger para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |