Austerity facts for kids
Austerity measures are actions governments take to save money. They are used when a country spends more than it earns. Governments might spend less, raise taxes, or do both. The main goal is to reduce the amount of money the government owes.
Contents
What are Austerity Measures?
Austerity measures are government plans to cut down on spending. They also aim to increase how much money the government collects. These plans are put in place when a country has a large budget deficit. A budget deficit means the government is spending more money than it brings in.
Why Governments Use Austerity
Governments use austerity when they find it hard to pay their debts. They want to bring their spending closer to their income. This helps to reduce the budget deficit. It also shows that the government is trying to be responsible with its money.
How Austerity Affects a Country
When governments cut spending, it can affect many areas. For example, there might be less money for public services. These services can include schools, hospitals, or roads. Raising taxes also means people and businesses have less money to spend.
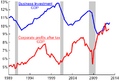
Impact on Jobs and Growth
Many economic experts believe that austerity can lead to more unemployment. When the government spends less, there might be fewer jobs in public services. Also, tax increases can reduce the money families have. This means people might buy fewer things. When people buy less, businesses might slow down.
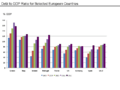
The Debt-to-GDP Ratio
Sometimes, cutting government spending can make a country's debt look even bigger. This is because government spending is part of a country's total economic output, called its GDP. If the economy shrinks due to austerity, the debt might seem larger compared to the smaller GDP. This is known as the debt-to-GDP ratio.
A Real-World Example
After a big economic downturn called the Great Recession, many European countries used austerity measures. Even though their budget deficits got smaller, unemployment often went up. Their debt-to-GDP ratios also sometimes increased. This shows that austerity can have complex effects on an economy.
Related pages
- Functional finance
- Neoliberalism
- Planned shrinkage
- Trickle-down economics
- Juice Rap News (April 2015). The EuroDivision Contest, a satire/parody of austerity
Images for kids
-
Relationship between fiscal tightening (austerity) in Eurozone countries with their GDP growth rate, 2008–12
See also
 In Spanish: Austeridad económica para niños
In Spanish: Austeridad económica para niños