B cell facts for kids
Quick facts for kids B cell |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| The cells of the immune system that make antibodies to invading pathogens such as viruses. They form memory cells that remember the same pathogen for faster antibody production in future infections. | |
| Latin | lymphocytus B |
| Code | TH H2.00.04.1.02005 TH H2.00.04.3.07002 |
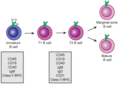
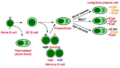
B cells are a special type of white blood cell called lymphocytes. They are a very important part of your body's adaptive immune system, which learns to fight off different germs. When a B cell gets activated, it changes into a plasma cell. This plasma cell then starts making special proteins called antibodies.
B cells have a unique protein on their outer surface called a 'B cell receptor'. This receptor acts like a tiny sensor. It allows the B cell to find and attach to a specific antigen. An antigen is a tiny part of something harmful, like a virus or bacteria.
What B Cells Do
B cells have several key jobs in your body:
- They make antibodies to fight against antigens. Antibodies are like tiny guided missiles that stick to invaders and mark them for destruction.
- They can act as antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This means they can show parts of an invader to other immune cells, helping the immune system learn what to attack.
- They develop into memory B cells after they have fought an infection.
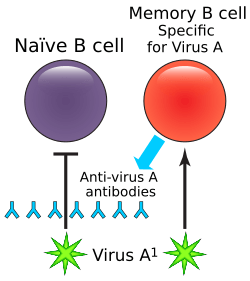
Memory B Cells
After a B cell has been activated and helped fight off an infection, some of them turn into "memory B cells." These memory cells are like a special library of past invaders. They remember the specific antigen they fought before. If that same invader tries to get into your body again, these memory cells quickly activate. They can then make antibodies much faster and stronger than the first time. This is why you often don't get sick from the same germ twice, or why vaccines work!
Where B Cells Come From
In humans and other mammals, new B cells are made in the bone marrow. This is a soft tissue inside your bones. The "B" in B cell actually comes from "bone marrow."
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Linfocito B para niños
In Spanish: Linfocito B para niños