Bitter pecan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Water hickory |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Unrecognized taxon (fix): | Carya sect. Apapocarya |
| Species: |
C. aquatica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carya aquatica (F.Michx.) Nutt.
|
|
 |
|
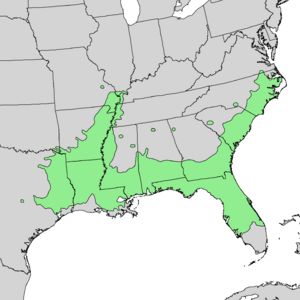
| Natural range of Carya aquatica | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Water Hickory (scientific name: Carya aquatica), also known as the bitter pecan, is a large tree. It belongs to the Juglandaceae family, which includes walnuts and pecans. These trees can grow very tall, sometimes over 30 meters (100 feet)!
In the Southern United States, water hickory trees are very common. They often grow in wet, flat areas near rivers and streams. This tree is tough and can grow well even in wet soils. It also helps clean water by slowing down floods. This allows dirt and other things in the water to settle.
Water hickory trees are important in wetland forests. They are good at growing back from seeds or from cut stumps. This helps them spread in areas where other trees might have been cut down for wood.
Contents
Where Water Hickory Lives
Native Home
Water hickory trees are found naturally in the eastern and southern parts of the United States. You can see them from southeastern Virginia down to southern Florida. They also grow west into eastern Texas and north along the Mississippi River Valley up to southern Illinois.
Soils and Land
Water hickory grows best in moist, well-drained soils. These soils are often found in river valleys and along streams. However, because these trees grow slowly, they are now more common in wet areas. In these wet spots, fewer other tree types can survive.
Water hickory trees are often found in clay flats and backwater areas. These places can flood during heavy rains. But they can also dry out and crack during hot, dry summers.
Forest Friends
Water hickory is a main tree in two types of forests. These are called "Sugarberry-American Elm-Green Ash" forests and "Overcup Oak-Water Hickory" forests. It can also be found in other forest types, like those with Sweetgum and Willow Oak.
Other important trees that grow with water hickory include:
- Overcup oak and Willow oak
- Cedar elm and American elm
- Waterlocust and honeylocust
- Pecan and green ash
- Sugarberry and persimmon
- Red maple and baldcypress
Some smaller trees and bushes often found with water hickory are hawthorn, swamp-privet, and buttonbush.
How Water Hickory Grows
Starting Life
Water hickory trees grow easily from seeds and sprouts. Seeds can start growing in disturbed soil or on the forest floor. Young trees need enough sunlight to grow big. Many water hickory forests today grew because other more valuable trees were cut down. This gave the water hickory more space and light.
Flowers and Fruit Water hickory trees have both male and female flowers on the same tree. These flowers appear in April and May, around the same time new leaves grow. The male flowers hang in long clusters. The female flowers are smaller and grow in short spikes.
The fruit of the water hickory has a thin shell and a bitter seed inside. These nuts fall from the tree between October and December.
Making Seeds Water hickory trees start making seeds when they are about 20 years old. They produce the most seeds between 40 and 75 years old. A healthy tree can produce a lot of seeds, sometimes up to 70 liters (about 2 bushels)!
Water and animals help spread the seeds. Floodwaters are especially good at carrying seeds to new places.
Young Trees After the seeds fall in autumn, they stay dormant until late April or early June. Most seeds only stay alive for one spring. Many seeds can sprout, sometimes almost 80% of them. This is why you might see thick groups of water hickory trees.
Young water hickory trees can survive in the shade for many years. But they need full sunlight to grow into tall trees. They grow slowly, so they need to be free from other plants competing for light. Water hickory seedlings can also survive late spring floods better than many other trees.
Growing from Sprouts If a water hickory tree is cut down, or its roots are cut, new sprouts can grow from the stump or roots. These sprouts grow much faster than seedlings in the first year or two. They can even grow up to 1.5 meters (5 feet) tall in their first year.
Growing Up
Growth and Size On good land, a water hickory tree can reach about 33.5 meters (110 feet) tall. Its trunk can be about 91 centimeters (3 feet) wide. The tree has a tall, straight trunk with branches that reach upwards.
Water hickory trees grow slowly in width, only about 2 to 8 millimeters (0.08 to 0.3 inches) per year. At 50 years old, a dominant tree might be about 35 centimeters (14 inches) wide on good land. On poor land, it might only be 25 centimeters (10 inches) wide.
Roots Like other hickory trees, water hickory starts with a deep taproot when it's young. But in the wet, clay soils where it often grows, the roots stay fairly shallow. The taproot eventually becomes the source of a wide, but shallow, root system.
Dealing with Competition Water hickory can handle some shade, but it's not the best at it. Because it grows slowly and its wood isn't as valuable, people often try to grow other tree species instead. However, when more valuable trees are cut down, water hickory often becomes more common.
If you want to reduce water hickory in a forest, cutting down larger trees can help. This allows faster-growing species to take over. But in some wet areas, water hickory will likely remain a major tree type. Also, projects that cause longer spring floods tend to help water hickory grow.
Things That Can Harm Water Hickory Insects can sometimes damage water hickory trees. The living-hickory borer is a common insect that attacks young trees. These borers make tunnels that can weaken the trunk. This makes the wood less valuable. Leaf-eating insects, like the forest tent caterpillar, can also sometimes eat all the leaves off the trees.
Diseases are usually not a big problem for water hickory. However, rot can get into the tree through wounds from fire or logging. This can make the wood unusable.
A common problem with water hickory wood is "shake," which means the wood splits easily. This is especially true for trees in waterlogged areas. Yellow-bellied sapsuckers (a type of bird) can also cause damage. Water hickory trees also tend to have more mistletoe growing on them than other trees.
Special Uses
The nuts of the water hickory are eaten by ducks, squirrels, wild hogs, and other wildlife. Sometimes, water hickory trees are planted or kept in natural areas for shade. The wood is also used locally as firewood and sometimes for fence posts.
The wet areas where water hickory grows are important. They help clean water and provide a safe home for many rare plants and animals.
Genetics
Scientists have not found different types (races) of water hickory. They also haven't studied much about how populations vary in different places. However, water hickory can mix with other hickory species to create hybrids. One common hybrid is Carya x lecontei, which is a mix of water hickory and pecan. Another hybrid is Carya x ludoviciana.
Images for kids
-
Pecan trees being irrigated in Anthony, New Mexico
See also
 In Spanish: Pecán para niños
In Spanish: Pecán para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |















