Block cipher facts for kids
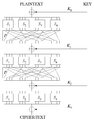
A block cipher is a special way to keep secret messages safe. It's like a secret code that works on chunks of information, not just one letter or bit at a time. Imagine you have a message. A block cipher takes a fixed-size piece of that message, scrambles it up, and turns it into a secret code. To unscramble it and get the original message back, you need a secret key.
For example, a block cipher might take a 128-bit chunk of your original message. It then uses a secret key to transform this chunk into a 128-bit chunk of scrambled code. When you want to read the secret message, the same key is used to turn the scrambled code back into the original message.
One of the first important block ciphers was the Data Encryption Standard (DES). It was created by IBM and became a standard in 1977. Later, a newer and stronger block cipher called the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) was chosen in 2001. AES is now widely used to protect our digital information.
Images for kids
-
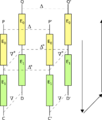
The boomerang attack is a special way to break certain codes. It helped cryptanalysts use differential cryptanalysis on codes that were thought to be safe before.
See also
 In Spanish: Cifrado por bloques para niños
In Spanish: Cifrado por bloques para niños