Broad-headed skink facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Broad-headed skink |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Scincidae |
| Genus: | Plestiodon |
| Species: |
P. laticeps
|
| Binomial name | |
| Plestiodon laticeps (Schneider, 1801)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
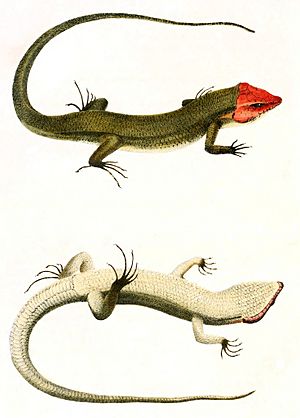
The broad-headed skink (Plestiodon laticeps) is a type of lizard that lives only in the southeastern United States. It gets its name from its wide head.
Contents
About Broad-Headed Skinks
What They Look Like
The broad-headed skink is one of the biggest types of Plestiodon skinks. It can grow from about 15 centimeters (6 inches) to almost 33 centimeters (13 inches) long.
These skinks are named for their wide jaws. This makes their head look a bit like a triangle. Adult males are usually brown or olive-brown. During spring, when they are ready to mate, their heads turn a bright orange color.
Female broad-headed skinks have five light stripes. These stripes run down their back and tail. Young skinks, called juveniles, are dark brown or black. They also have stripes and a bright blue tail.
Where They Live
Broad-headed skinks prefer to live in damp forest areas. They especially like oak forests with lots of fallen leaves. You might also find them in some city areas.
How They Behave
Broad-headed skinks are very good at climbing trees. They are the best climbers among the North American Plestiodon skinks. They often climb trees to find shelter, sleep, or look for food. While they climb trees a lot, they also search for food on the ground.
How They Reproduce
Male broad-headed skinks are usually bigger than females. A larger female can lay more eggs. Because of this, males often try to mate with the biggest females they can find. Sometimes, males will even fight each other to get to a female.
A female skink lays between 8 and 22 eggs. She stays with her eggs and protects them. The eggs usually hatch in June or July. When they hatch, the baby skinks are about 6 to 8 centimeters (2.4 to 3.1 inches) long.
Where They Are Found
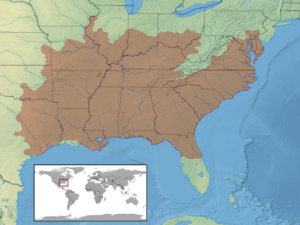
Broad-headed skinks live across many southeastern states in the United States. Their home range stretches from the East Coast all the way to Kansas and eastern Texas. They can also be found from Ohio down to the Gulf Coast.
Are They Dangerous?
No, broad-headed skinks are not dangerous. They are sometimes mistaken for venomous animals, but they are completely nonvenomous. This means they do not have any poison.
See also
 In Spanish: Eslizón de cabeza ancha para niños
In Spanish: Eslizón de cabeza ancha para niños