Torchwood copal facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Torchwood copal |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Burseraceae |
| Genus: | Bursera |
| Species: |
B. fagaroides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bursera fagaroides (Kunth) Engl. 1880
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
Elaphrium fagaroides Kunth 1824
Amyris fagaroides Spreng. Amyris ventricosa La Llave ex Schltdl. Bursera covillei (Rose) Engl. Bursera inaguensis Britton Bursera lonchophylla Sprague & L.Riley Bursera obovata Turcz. Bursera odorata Brandegee Bursera purpusii Brandegee Bursera schaffner S.Watson Commiphora inaguensis (Britton) M.Moncada Ferrera Elaphrium covillei Rose Elaphrium inaguense (Britton) Rose Elaphrium lonchophyllum (Sprague & Riley) J.G.Ortega Elaphrium obovatum (Turcz.) Rose Elaphrium odoratum (Brandegee) Rose Elaphrium purpusii (Brandegee) Rose Elaphrium schaffneri (S.Watson) Rose Elaphrium tenuifolium Rose Terebinthus fagaroides (Kunth) Rose Terebinthus inaguensis Britton Terebinthus odorata Rose Terebinthus schaffneri (S. Watson) Rose Terebinthus tenuifolia (Rose) Rose |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
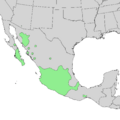
Bursera fagaroides is a cool plant known as the torchwood copal or fragrant bursera. It's a type of tree or shrub found mostly in Mexico. You can also find it in a small part of Arizona in the United States. Some people think it might not grow in Arizona anymore.
This plant belongs to the Bursera family. It is similar to the elephant tree, but you can tell them apart. The torchwood copal has longer and thinner leaves.
Contents
About the Torchwood Copal Tree
What Does It Look Like?
The torchwood copal can grow quite tall, up to 10 meters (about 33 feet). Its trunk is a bit swollen and has bark that peels off. This bark often has a reddish color.
The leaves of the tree are made up of smaller leaflets. Each leaf usually has between 5 and 11 of these small leaflets.
The flowers are white, sometimes with a hint of yellow or green. They grow alone or in small groups at the ends of the branches. After the flowers, the tree produces fruit. The fruit is gray-brown and shaped like a triangle. It's about 6 millimeters long. When the fruit is ready, it splits open to let out a reddish seed.
Where Does It Grow?
This plant likes to grow in the dry areas of the Sonoran Desert. Farther south in Mexico, you can find it in dry riverbeds called arroyos. It grows in places with shallow soil and lots of rocks, especially limestone.
Who Eats Its Seeds?
Birds love to eat the seeds of the torchwood copal. For example, the white-eyed vireo and the grey catbird enjoy these seeds.
How People Use This Plant
People grow Bursera fagaroides as an ornamental plant. This means it's grown just because it looks nice. It can even be shaped into a bonsai tree, which is a small, carefully grown tree.
In Mexico, people have used the sticky gum from this tree. They used it to help treat stings from scorpions and bites from insects.
Gallery
See also
 In Spanish: Bursera fagaroides para niños
In Spanish: Bursera fagaroides para niños
 | Lonnie Johnson |
 | Granville Woods |
 | Lewis Howard Latimer |
 | James West |