Bronze-tailed thornbill facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bronze-tailed thornbill |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Chalcostigma
|
| Species: |
heteropogon
|
 |
|
The bronze-tailed thornbill (Chalcostigma heteropogon) is a small, colorful hummingbird. It lives in the high mountains of Colombia and Venezuela. This bird is known for its unique bronze-colored tail.
Contents
About the Bronze-tailed Thornbill
The bronze-tailed thornbill is about 13 to 14 centimeters (5 to 5.5 inches) long. It weighs around 6 grams (0.2 ounces), which is very light! Both male and female birds have a short, straight black beak.
Most of their body is a shiny bottle green color. Their upper tail feathers are coppery red, and their tail is olive green and forked.
Male vs. Female Birds
Male bronze-tailed thornbills have a special patch of feathers under their chin called a gorget. This gorget is emerald green near the chin and turns pink at the bottom. It looks like a tiny, colorful beard!
Female birds look similar to males. However, their gorget is a lighter green and does not have the pink part. Also, the outer feathers of their tail have pale tips. Young birds look like adult females, but they have a reddish-brown crown on their head.
Where They Live
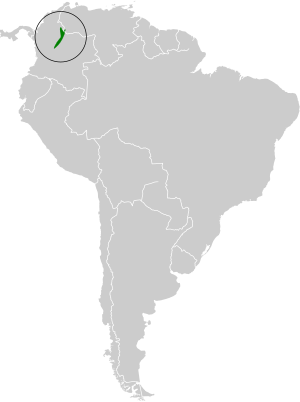
The bronze-tailed thornbill lives in the Andes mountains. You can find them from the Tamá Massif in western Venezuela, all the way through the Eastern Andes of Colombia. They live in places like the Cundinamarca Department.
These birds prefer steep, rocky slopes. They live in grasslands that can be dry or humid, called páramo. They also live at the edges of small forests, especially those with Polylepis trees. They are found at very high elevations, usually between 3,000 and 3,900 meters (9,800 to 12,800 feet) above sea level.
How They Behave
Bird Movements
Scientists believe that bronze-tailed thornbills usually stay in the same area. However, they might move up or down the mountains depending on the season.
What They Eat
Bronze-tailed thornbills mostly eat nectar from different flowers and shrubs. They get nectar by clinging to flowers or hovering in front of them. Unlike some other thornbills, they don't usually feed on the ground.
Both male and female birds are quite protective of their feeding spots. They will defend patches of flowers from other birds! They also eat insects. They pick insects off plants or catch them while flying.
Breeding and Young Birds
The breeding season for the bronze-tailed thornbill is thought to be from September to January. It might even be longer. Like other hummingbirds, the female bird builds the nest and lays two white eggs. She is the only one who sits on the eggs to keep them warm. Not much else is known about how they raise their young.
Bird Calls
The bronze-tailed thornbill makes a short, dull call that sounds like "tzk." Scientists are not sure if they make any other sounds.
Their Safety Status
The bronze-tailed thornbill is currently listed as a species of "Least Concern" by the IUCN. This means they are not in immediate danger of disappearing. However, they live in a specific area, and their total number of birds is unknown. It is believed that their population might be getting smaller.
These birds live in some protected areas. The high altitude and tough climate of their home also help protect them from people. But, the Polylepis woodlands where they live are becoming damaged in many parts of their range.
See also
 In Spanish: Colibrí picoespina para niños
In Spanish: Colibrí picoespina para niños


