Chemical kinetics facts for kids
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of how fast chemical reactions happen. It helps scientists understand what makes reactions speed up or slow down. This includes looking at how things like heat (temperature), pressure, or the liquid a reaction takes place in (called a solvent) can change how quickly a reaction occurs.
This field also helps scientists figure out the exact steps a reaction takes, which is called its reaction mechanism.
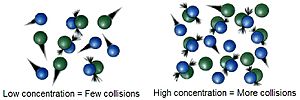
The main idea behind chemical kinetics is called the collision theory. This theory says that for a chemical reaction to happen, the tiny particles (molecules) involved must bump into each other. To make a reaction go faster, you need more of these bumps. This can be done in many ways, like increasing the amount of starting materials (concentration) or raising the temperature.
Scientists do experiments to figure out how fast reactions go. From these experiments, they can create 'rate laws' and 'rate constants'. A rate law is a math rule that helps you predict how fast a reaction will be, based on how much of the starting materials (reactants) you have.
Understanding Reaction Speed
When we talk about how fast a reaction goes, we often use the term "reaction rate." This rate can be influenced by several factors:
- Concentration: If you have more molecules in the same space, they are more likely to bump into each other. This usually makes the reaction faster.
- Temperature: When you heat things up, molecules move faster. Faster movement means more collisions and more energetic collisions, leading to a faster reaction.
- Pressure: For reactions involving gases, increasing the pressure pushes the gas molecules closer together. This increases the chance of collisions and speeds up the reaction.
- Surface Area: If a reaction happens on a surface, breaking a solid into smaller pieces increases its surface area. This gives more places for molecules to react, making the reaction faster.
- Catalysts: A catalyst is a special substance that speeds up a reaction without being used up itself. It helps molecules react more easily.
Order of a Reaction
Scientists classify reactions based on how their speed depends on the amount (concentration) of the starting materials. This is called the "order" of the reaction.
There are a few common types:
- Zero-order reaction: The speed of this reaction does not change, no matter how much of the starting material you have. It stays constant.
- First-order reaction: The speed of this reaction depends on the concentration of only one starting material. If you double that material, the reaction speed doubles.
- Second-order reaction: The speed of this reaction depends on the concentration of two different starting materials, or on the concentration of one starting material squared.
By studying the order of a reaction, scientists can learn about its mechanism. For example, if a reaction is second-order, it often means that two molecules must come together in the slowest step of the reaction. This slowest step is called the rate-determining step. It's the most difficult part of the reaction because it needs the most energy to happen (called activation energy).
See also
In Spanish: Cinética química para niños