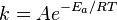Activation energy facts for kids

The activation energy of a chemical reaction is the smallest amount of energy needed for that reaction to begin. Think of it like a small hill or barrier that chemicals need to climb over before they can change into new substances. This energy is often shown with the symbol Ea and is measured in kilojoule per mole.
Contents
How Reactions Get Started
Imagine you want to push a ball up a small hill. You need to give the ball enough energy to reach the top. Once it's over the top, it can roll down the other side easily. In the same way, chemical reactions need a push of energy to get started. This push is the activation energy. Without enough activation energy, the chemicals might just sit there and not react.
Understanding Reaction Speed
Scientists use an equation called the Arrhenius equation to understand how fast a chemical reaction happens. This equation helps them see how temperature and activation energy affect the speed of a reaction.
The equation looks like this:
- k is the reaction rate, which tells us how fast the reaction is going.
- A is a factor that depends on how often molecules bump into each other.
- R is the gas constant, a number used in physics.
- T is the temperature of the reaction.
By measuring how fast a reaction goes at different temperatures, scientists can use this equation to figure out the activation energy. Generally, if you increase the temperature, more molecules have enough energy to overcome the activation energy, making the reaction go faster.
Catalysts: Reaction Shortcuts
Sometimes, we want a reaction to happen faster without raising the temperature a lot. This is where a catalyst comes in handy. A catalyst is a special substance that speeds up a chemical reaction.
How do catalysts work? They lower the activation energy. Imagine our hill again. A catalyst is like building a tunnel through the hill or creating a much smaller path. This means the chemicals need less energy to start reacting, so the reaction happens much more quickly.
It's important to know that a catalyst itself does not get used up in the reaction. This means a small amount of catalyst can be used over and over again. Catalysts also do not change the starting energy of the chemicals or the final energy of the products. They only provide an easier path for the reaction to take.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Energía de activación para niños
In Spanish: Energía de activación para niños