Cochlea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Cochlea |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
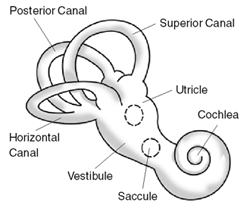
| The inner ear or bony labyrinth includes the cochlea for hearing and the vestibular organs for balance. | |
 |
|
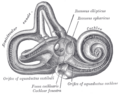
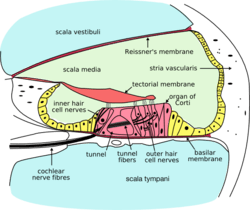
| Cross section of the cochlea. | |
| Gray's | subject #232 1050 |
| MeSH | Cochlea |
The cochlea is a super important part of your inner ear. It's shaped like a snail shell! This amazing part of your ear helps you hear sounds. Inside, there's a special part called the Organ of Corti. It's the main "hearing organ" and is found along the tubes inside the cochlea. Only mammals, like humans, have a cochlea shaped like this.
The word "cochlea" comes from Latin. It means "snail" or "snail shell." This makes sense because of its cool spiral shape!
Contents
How the Cochlea is Built
The cochlea is a hollow, spiral-shaped bone chamber. Think of it like a tiny, winding tunnel. Inside this tunnel are three main fluid-filled sections:
- The scala vestibuli is the top section. It contains a fluid called perilymph. This section starts near the oval window, which is a small opening from your middle ear.
- The scala tympani is the bottom section. It also contains perilymph. This section ends at the round window.
- The scala media is the middle section. It contains a different fluid called endolymph. This is where the Organ of Corti is located.
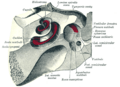
Key Parts Inside
- The helicotrema is the tiny tip of the spiral. It's where the scala vestibuli and scala tympani connect.
- Reissner's membrane is a thin wall. It separates the scala vestibuli from the scala media.
- The basilar membrane is another important wall. It separates the scala media from the scala tympani.
- The Organ of Corti is the main hearing part. It sits on the basilar membrane. This organ has special sensory cells called hair cells. These cells have tiny, hair-like structures on top called stereocilia.
How the Cochlea Helps You Hear
The cochlea is filled with a watery liquid. When sounds vibrate your eardrum, these vibrations travel to the middle ear bones. These bones then push on the oval window of the cochlea. This makes the fluid inside the cochlea move.
Hair Cells and Signals
As the fluid moves, thousands of tiny "hair cells" inside the Organ of Corti start to move too. This movement is super important! The hair cells change this motion into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to many thousands of nerve cells.
These nerve cells turn the signals into electrical impulses. These impulses travel along the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve then sends these messages to your brain. Your brain then figures out what the sounds are!
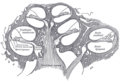
Inner and Outer Hair Cells
The hair cells are arranged in four rows inside the cochlea.
- Three rows are called outer hair cells (OHCs). These cells mainly get signals from your brain. They help to make sounds louder and clearer.
- One row is called inner hair cells (IHCs). These are the main cells that send hearing signals from your ear to your brain.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Cóclea para niños
In Spanish: Cóclea para niños