Inner ear facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Inner ear |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
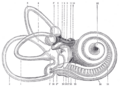
| The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above. | |
| Latin | auris interna |
| Artery | labyrinthine artery |
The inner ear is the deepest part of your ear. It's a super important part of your body that helps you hear sounds and keep your balance. Think of it as a tiny, amazing control center inside your head!
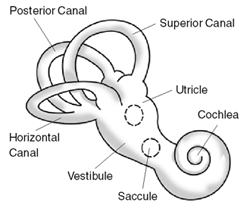
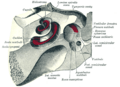
In mammals, like humans, the inner ear has two main parts. These parts are tucked away inside a bony maze called the labyrinth.
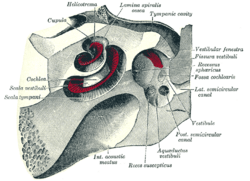
- The cochlea (say: KOK-lee-uh) is all about hearing. It takes sound vibrations from your outer ear and turns them into electrical signals. These signals then travel to your brain, so you can understand what you hear.
- The balance system helps you stay upright and know where you are in space. It has three special loops called semi-circular canals. These canals are set at right angles to each other, like the corners of a box.
The inner ear is found in all animals with a backbone, called vertebrates. Even though it looks a bit different in various animals, it always helps with hearing and balance. The inner ear is connected to the brain by a special wire-like structure called the eighth cranial nerve.
Contents
How Your Inner Ear Helps You Hear
The Cochlea: Your Ear's Sound Processor
The cochlea is shaped like a snail shell. It's filled with fluid and tiny hair cells. When sound waves reach the cochlea, they make the fluid move. This movement bends the hair cells.
When the hair cells bend, they create electrical signals. These signals are then sent to your brain through the auditory nerve. Your brain then figures out what those signals mean, and that's how you hear music, voices, or anything else!
Keeping Your Balance: The Vestibular System
The Semi-Circular Canals: Your Body's Gyroscopes
Your inner ear also has a special system for balance, called the vestibular system. A big part of this system is the three semi-circular canals. These canals are filled with fluid and have tiny hair cells, just like the cochlea.
When you move your head, the fluid inside these canals also moves. This movement bends the hair cells, sending signals to your brain. Your brain uses these signals to know if you're turning, tilting, or moving up and down. This helps you stay balanced and not fall over!
The Otolith Organs: Sensing Gravity and Movement
Besides the semi-circular canals, the balance system also has two small sacs called the utricle and saccule. These are sometimes called the otolith organs. They have tiny calcium carbonate crystals, like little stones.
These "ear stones" move when you tilt your head or when you speed up or slow down. This movement tells your brain about gravity and straight-line movements, like when you're riding in a car or an elevator. Together, all these parts of your inner ear work to give your brain a complete picture of your body's position and movement.
Images for kids
-
The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above.
See also
 In Spanish: Oído interno para niños
In Spanish: Oído interno para niños