Cognitive distortions facts for kids
Cognitive distortions are unhelpful or exaggerated thoughts. These thoughts can make some mental challenges feel worse. When people follow these thinking patterns, it can be hard for them to do what they want. This can sometimes lead to problems like feeling very sad or worried. Learning about these thoughts can help you understand them better.
Contents
Understanding Thinking Traps
Cognitive distortions are like "thinking traps." They are ways our minds can trick us into believing things that are not completely true. These thoughts can make us feel bad or stop us from trying new things. Recognizing these traps is the first step to changing them.
Common Thinking Traps
There are many types of cognitive distortions. Here are some common ones:
All-or-Nothing Thinking
This is when you see things as only good or only bad. There is no middle ground. For example, if you don't get a perfect score on a test, you might think you failed completely. This is also called "black-and-white thinking."
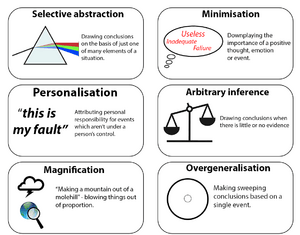
Overgeneralization
When you overgeneralize, you make a big conclusion based on just one or two events. You might think that if something bad happened once, it will always happen. For example, if you have one bad day, you might think, "My whole life is always terrible."
Filtering Out the Positive
This trap makes you focus only on the bad things. You might ignore all the good things that happen. Even if many good things happen, you only remember the one small negative thing.
Mind Reading
Mind reading is when you think you know what others are thinking. You believe their thoughts are negative, even without proof. For example, you might think, "They think I'm silly," without asking them.
Fortune Telling
This is when you try to guess the future. You believe your negative guesses are facts. For example, you might think, "I'm going to fail this presentation," before you even start.
Emotional Reasoning
With emotional reasoning, you believe your feelings are facts. If you feel sad, you think, "I feel sad, so things must be truly awful." Your feelings become the truth, even if there's no other evidence.
Should Statements
These are thoughts about how you "should" or "must" act. If you don't meet these strict rules, you might feel guilty or ashamed. For example, "I should always be perfect."
Labeling
Labeling is when you give yourself or others a general, negative tag. Instead of saying, "I made a mistake," you might say, "I am a loser." These labels don't really describe the whole person.
Personalization
Personalization is when you think you are responsible for everything that goes wrong. You might blame yourself for things that are not your fault. For example, "It's my fault the team lost."
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Distorsión cognitiva para niños
In Spanish: Distorsión cognitiva para niños

