Colorfulness facts for kids

Colorfulness, chroma, and saturation are all terms that describe how strong or vivid a color appears. They help us understand how we see colors. While these words are often used to mean the same thing, they actually describe slightly different aspects of a color's intensity.
- Colorfulness is how much a color seems "colorful" to your eyes. Imagine a bright red apple; it looks very colorful. This depends on how bright the light is. The brighter the light, the more colorful an object usually appears.
- Chroma describes how different a color is from a gray color that has the same brightness. It's like saying, "How much pure color is there, compared to a neutral gray?" Chroma helps describe the true color of an object, no matter how bright the light is.
- Saturation is how much a color is free from any whitishness. Think of a pure, deep blue. It has high saturation. If you add white to it, it becomes less saturated. An object's saturation usually stays about the same, even if the light changes.
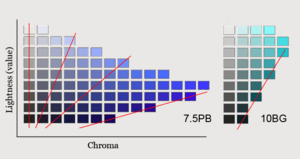
These terms describe how we perceive colors. We can't measure them with a ruler. But we can use special color systems, like the Munsell color system, to compare and organize colors based on their chroma and other qualities.
What is Chroma?
Chroma is a way to measure how intense or pure a color is. It tells you how much a color stands out from a neutral gray. A color with high chroma looks very vivid and strong. A color with low chroma looks dull or muted, closer to gray.
For example, a bright red fire truck has high chroma. A faded pink shirt has low chroma. Chroma helps us describe the "true" color of an object. It's like saying how much "color" is really there, compared to just brightness or darkness.
What is Saturation?
Saturation describes how much pure color is in a light. Think of a laser beam; it's made of just one color of light, so it's very saturated. If the light isn't as strong, its saturation goes down.
You can change a color's saturation in different ways:
- Adding white, black, or gray to a color makes it less saturated.
- Adding a color's opposite color (like adding green to red) also makes it less saturated.
In some color systems, like HSL and HSV, saturation is a separate control. This means you can have a very light color or a very dark color that is still highly saturated. In other systems, colors that are very light (close to white) or very dark (close to black) naturally have lower saturation.
Excitation Purity
Excitation purity is another way to describe how pure a color is. It measures how far a color is from the white point on a color diagram. Imagine a line from the center (white) to the edge of the color spectrum. Excitation purity tells you how far along that line your color is. A color right on the edge of the spectrum is very pure. A color closer to the center (white) is less pure.
See also
 In Spanish: Saturación (color) para niños
In Spanish: Saturación (color) para niños
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |







