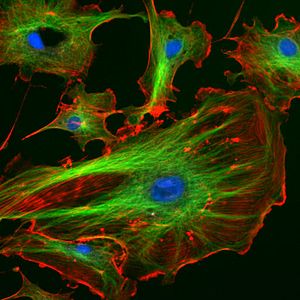
Cytoskeleton facts for kids
The cytoskeleton is like the internal framework or "skeleton" of a cell. It's made of tiny protein parts. This amazing structure helps cells keep their shape, protects them, and even allows them to move around!
What Does the Cytoskeleton Do?
The cytoskeleton has many important jobs inside a cell. Think of it as a busy construction crew!
- Keeps Cell Shape: Just like your bones give your body shape, the cytoskeleton helps cells keep their unique form. This is super important because different cell shapes help them do different jobs.
- Protects the Cell: It acts like a protective shield, helping the cell withstand pressure and stay strong.
- Helps Cells Move: Some cells need to move from one place to another. The cytoskeleton helps them do this using special structures like flagella (tail-like parts) and cilia (tiny hair-like parts).
- Transports Things Inside: Imagine a tiny highway system inside the cell. The cytoskeleton helps move important packages, like vesicles (small sacs) and organelles (cell parts), from one place to another within the cytoplasm (the jelly-like substance inside the cell).
- Aids Cell Division: When a cell needs to make copies of itself, the cytoskeleton plays a key role in pulling the new cells apart correctly.
The idea of the cytoskeleton was first introduced by a French scientist named Paul Wintrebert in 1931. He called it "cytosquelette."
The Three Main Parts
In eukaryote cells (which include animal, plant, and fungi cells), the cytoskeleton is made of three main types of protein threads, or filaments:
- Microfilaments (Actin Filaments): These are the thinnest parts. They are made of a protein called actin. Microfilaments are very important for cell movement, muscle contraction, and changing cell shape.
- Intermediate Filaments: These are a bit thicker than microfilaments. They provide strong support and help the cell resist stretching and pressure. They are like strong ropes that hold the cell together.
- Microtubules: These are the thickest parts of the cytoskeleton. They are hollow tubes that act like tracks for transporting things inside the cell. They also help build structures like cilia and flagella, and play a big role in cell division.
These different parts of the cytoskeleton work closely together. They also connect with the cell membrane (the outer skin of the cell) and the endoplasmic reticulum (another important cell organelle) to make sure the cell functions smoothly.
See also
 In Spanish: Citoesqueleto para niños
In Spanish: Citoesqueleto para niños