Diadem leaf-nosed bat facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Diadem leaf-nosed bat |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| photograph taken by Michael Pennay | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Hipposideridae |
| Genus: | Hipposideros |
| Species: |
H. diadema
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hipposideros diadema (É. Geoffroy, 1813)
|
|
 |
|
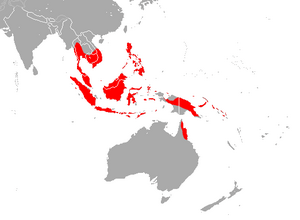
| Diadem roundleaf bat range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The diadem leaf-nosed bat or diadem roundleaf bat (Hipposideros diadema) is a type of bat found in many places. It belongs to the family Hipposideridae. This bat is closely related to Hipposideros demissus from Makira and Hipposideros inornatus from Australia. You can find Hipposideros diadema in countries like Australia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Contents
What the Diadem Bat Looks Like
The diadem bat gets its name from its unique nose. It has a special horseshoe-shaped nose leaf. This nose leaf helps the bat use echolocation better. Echolocation is like sonar, where bats send out sounds and listen for echoes to find things.
The nose leaf stands up and doesn't have a middle bump. These bats also have very large ears. Their ears have a well-developed part called an antitragus, but they don't have a tragus.
Male bats have a special sac behind their nose. This sac makes a waxy substance. Scientists think this substance helps males attract mates or show their status.
Adult diadem bats are about 6 to 10 centimeters long. Their fur is brown, but their belly is lighter. They often have white spots on their shoulders. They weigh between 34 and 50 grams. Their wingspan is about 15 to 22 centimeters.
They have strong claws on their back feet. Each front limb has one claw. Their short tail is usually hidden within a small membrane called the uropatagium.
How Diadem Bats Reproduce
Diadem bats have one breeding season each year. They give birth and feed their young when there are lots of insects. This usually happens in the spring. Each mother bat gives birth to one baby at a time.
Male bats compete to find mates. They might have small fights, but mostly they use the waxy substance from their nose sac. Female bats gather in large groups in March and April. This is when they give birth to their single offspring. The mother stays close to her baby until it can feed itself. After that, the young bat usually becomes independent.
Where Diadem Bats Live and Hunt
The diadem bat has a heavy body and long, narrow wings. This helps it fly fast. However, it's not very good at quick turns. It prefers to hunt in open areas within forests. This includes places like gaps where trees have fallen or above rivers.
These bats don't only live in rainforests. In Australia, they also hunt in eucalyptus woodlands and open forests. They can even be found in towns. They are known to fly up to 2.5 kilometers from their roosting spot at night to find food.
During the day, they rest in small groups. They sleep in caves, old mines, sheds, hollow trees, and even on tree branches.
How Long Diadem Bats Live
Diadem bats usually live for about four to seven years in the wild. If they are kept in captivity, like in a zoo, they can live much longer. Some have lived up to twelve years.
Diadem Bat Behavior
These bats are active at night, which means they are nocturnal. They are also very social animals. They live together in large groups called colonies. These colonies can have as many as two to three thousand bats!
While they live in groups, each colony seems to have its own territory. It's very rare for these bats to attack humans. But if they feel threatened or cornered, they can bite. Their bite can be painful. These bats can carry many parasites, but most of them do not affect humans.
What Diadem Bats Eat
Diadem bats mostly eat insects. Their diet changes depending on where they live. They especially like beetles, butterflies, moths, and grasshoppers. Sometimes, they will also eat small birds and spiders, but this is rare. Because of this, they are sometimes called occasional carnivores.
These bats are very skilled hunters. They use echolocation, which is made even better by their special nose and nostrils. This helps them catch prey very successfully. They send out a constant sound call, usually between 50 to 58 kilohertz (kHz). They can keep this call going for 20 to 30 seconds at a time.
Diadem bats don't hunt by flying continuously. Instead, they prefer to take short flights from a perch. They catch their prey in mid-air. This "perch hunting" is a low-energy way for them to find food. When they hunt, they often fly over streams or creeks that are covered by trees. They rarely fly over open water.
Moths, especially those with ears, are a big part of their diet. These moths can hear the bats' echolocation pulses. They have learned to avoid or hide from the attacking bats. Besides beetles and moths, diadem bats also eat weevils and katydids. They eat the soft parts of these insects and leave behind the hard parts like wings and legs.


