Digital signal processor facts for kids
A digital signal processor (often called a DSP) is a special type of microprocessor. Think of it as a tiny computer chip made to handle specific tasks very quickly. Its main job is to work with digital signal processing. This means it takes information, like sounds or images, and changes it using math. DSPs are often used for things that need to happen right away, which is called real-time computing.
Contents
What is a Digital Signal Processor?
A DSP is like a super-fast calculator for signals. Signals are things like sound waves from your voice, music, or even radio waves. In the real world, these signals are usually analog. This means they are continuous, like a smooth wave. But computers need information to be digital, which means it's broken down into numbers (like 0s and 1s).
How DSPs Work
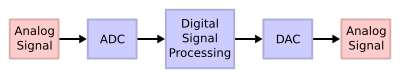
Here's how a DSP usually works:
- First, an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) takes an analog signal and turns it into a digital signal. Imagine taking a smooth drawing and turning it into tiny dots of color, each with a number.
- Next, the DSP chip gets to work. It uses special math steps, called algorithms, to change this digital information. For example, it might clean up noise from a sound, add effects to music, or compress a video file to make it smaller.
- Finally, a DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter) takes the processed digital signal and turns it back into an analog signal. This lets you hear the improved sound or see the clear image.
Many things that use DSPs need to happen instantly. For example, when you talk on a phone, the DSP needs to process your voice so quickly that the person on the other end hears you without delay. This is why DSPs are designed to be very fast at doing lots of math operations.
Where are DSPs Used?
DSPs are found in many everyday devices. They help make our digital world work smoothly.
- Mobile phones: They process your voice, handle noise cancellation, and manage wireless signals.
- Music players: They improve sound quality and add special audio effects.
- Digital cameras: They process images, making them clearer and more colorful.
- Medical equipment: Like MRI machines, they process complex signals to create detailed images of the body.
- Car systems: They can help with things like active noise cancellation in cars or advanced driver-assistance systems.
The special design of a DSP chip makes it perfect for these kinds of tasks. It's built to handle the specific math needed for digital signal processing much faster than a regular computer processor could.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
A TMS320 digital signal processor chip found in a guitar effects unit. You can see a crystal oscillator above it.
See also
 In Spanish: Procesador de señales digitales para niños
In Spanish: Procesador de señales digitales para niños