Disk partitioning facts for kids
Disk partitioning is like dividing a big cake into smaller slices. In computers, it means splitting your computer's storage (like a hard drive) into separate sections. These sections are called partitions. Each partition acts like its own mini-storage area.
When you get a new computer or a new hard drive, partitioning is usually the first step. It helps you organize your disk before you put any files on it. Your computer stores information about these partitions in a special area called the partition table. This table tells the computer where each partition starts and how big it is.
Think of each partition as a separate "logical" disk. This means your computer sees them as individual drives, even though they are all on the same physical hard drive. Computer experts use special programs called partition editors to create, change, or delete these partitions.
Partitioning has some cool benefits:
- You can use different ways of organizing files (called file systems) on different partitions.
- It helps keep your important system files separate from your personal files. This stops your computer from slowing down if your personal files take up too much space.
- It can make backing up your data easier, as you can back up specific sections.
One small challenge is figuring out the right size for each partition. Sometimes, one partition might have too much empty space, while another fills up too quickly.
Contents
How Disk Partitioning Started
The idea of dividing a disk into smaller parts isn't new. Back in 1966, IBM used something called a minidisk to split up their hard drives.
Later, in 1983, IBM released a computer operating system called PC DOS version 2.0. This system used the word partition to describe dividing a hard drive into physical sections. Since then, the word "partition" has become very common. You might also hear terms like logical disk or slice to describe these sections.
Different Ways to Partition Disks
Computers use different methods, or "schemes," to organize partitions.
How Windows and Older Systems Partition Disks
With Windows computers, it's common to have one main partition. This partition usually holds the operating system (like Windows itself), all your programs, and your personal files. This main partition is often called the C: drive.
Sometimes, there are other hidden partitions on the hard drive. These might be for recovering your system if something goes wrong or for special diagnostic tools. Windows has a built-in tool called 'Disk Management' that lets you create, delete, and change partitions.
How Unix-like Systems Partition Disks
Operating systems like Linux and macOS (which are "Unix-like") often use multiple partitions on a single disk. Each partition can be set up with its own file system or used for special purposes like "swap space" (which helps your computer use memory more efficiently).
Using multiple partitions has several advantages:
- If one part of your file system gets damaged, the rest of your data on other partitions might stay safe. This helps prevent losing all your files.
- You can set up different partitions with special rules. For example, some might be "read-only" to prevent accidental changes.
- If a program goes wild and fills up one partition, it won't fill up the critical system files on another partition.
- Keeping your personal documents separate from system files makes it safer to update your computer.
A common setup for Linux computers is to have three partitions: one for the main system files, one for user files (like your documents and pictures), and a swap partition. macOS systems usually use one main partition for everything, similar to Windows.
In some systems like Solaris, partitions are called slices, like cutting a cake into pieces.
Running Multiple Operating Systems
Some computers are set up as multi-boot systems. This means you can choose to start your computer with more than one operating system. For example, you might have both Windows and Linux installed on different partitions of the same hard drive.
When you turn on a multi-boot computer, a special menu appears. This menu lets you pick which operating system you want to use for that session. You can only run one operating system at a time this way. This is different from "virtual machines," where one operating system runs inside another as a program.
GUID Partition Table (GPT)
The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a newer and more modern way to organize partitions on a hard drive. It's part of a standard called UEFI, which helps computers start up. Many modern operating systems support GPT. It's generally better than older methods because it can handle much larger disks and more partitions.
Getting Back Lost Partitions
If a partition is accidentally deleted, its information is removed from the partition table. This makes the data on it seem "lost" because the computer doesn't know where it is anymore. However, the actual data often remains on the disk until something new is written over it.
Special recovery tools can sometimes find these "lost" file systems and rebuild the partition table. This can help you get your data back. But be careful, as some tools might overwrite the beginning of a deleted partition, making recovery harder.
Compressed Disks
In the past, especially with older versions of Windows, people used programs to "compress" their hard drives. This made it seem like they had more space. These programs would create a very large file on a partition and then store all the disk's data inside that compressed file.
Modern versions of Windows (like Windows 10) have their own built-in disk compression features. Because of this, separate disk compression programs are not used much anymore.
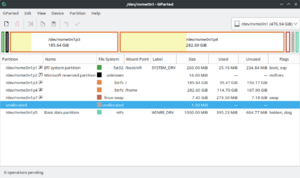
What is a Partition Table?
A partition table is like a map on your hard drive. It's a special table that the operating system uses to keep track of all the partitions on that disk. It shows where each partition is located and how big it is.
The most common partition table for older PCs is called the Master Boot Record (MBR) partition table. Newer computers often use the GUID Partition Table (GPT). Other types exist too, like Apple partition maps.
Types of PC Partitions
Historically, on PC computers, the MBR partitioning scheme was very common. However, most new computers today use the GUID Partition Table (GPT) instead.
With MBR, a hard drive could have up to four primary partitions. Or, it could have three primary partitions and one extended partition. The partition table, located in a special area called the master boot record, holds small entries that describe each partition.
Each partition has a special 1-byte code that tells the computer what type of partition it is. This code helps the operating system know if it can use the partition to store files or if it has a special purpose.
Primary Partitions
A primary partition usually contains one file system. In older Windows systems, the main operating system partition had to be the first primary partition. Modern Windows versions are more flexible, but the important "boot files" (which help the computer start) still need to be on a primary partition.
The type code for a primary partition tells the computer what kind of file system is on it. For example, a code might mean it's an NTFS file system (common for Windows) or a Linux file system.
Extended Partitions
A hard drive can only have one extended partition. However, this extended partition can be divided into many smaller logical partitions. This allows you to have more than four sections on your hard drive if you need them. Modern GPT disks don't use extended or logical partitions; they just have primary partitions.
Boot Partitions
There are special partitions used to help your computer start up:
BIOS Boot Partition
This is a small part of the storage device that holds the software needed to start the operating system. It might contain a "bootloader," which is a small program that helps load the main operating system.
EFI System Partition
This is similar to a BIOS boot partition but is used by newer computer systems that use EFI firmware instead of the older BIOS system.
See also
- Disk formatting
- List of disk partitioning software
- Master boot record
- RAID
Images for kids