Displacement (geometry) facts for kids
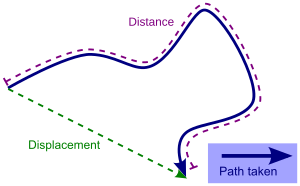
In geometry and physics, displacement is a special kind of measurement. It tells you how far an object has moved from its starting point to its ending point, and in what direction. Think of it as the shortest straight line from where you began to where you finished.
For example, if you walk around a block and end up back where you started, your total distance walked might be 400 meters. But your displacement is zero, because your final position is the same as your initial position! Displacement helps us understand the overall change in an object's location.
We can describe displacement using a vector. A vector is a quantity that has both a size (like 5 meters) and a direction (like "north").
You can find the displacement (often called s) by subtracting the starting position (xi) from the final position (xf). 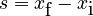
When objects move, their displacement changes over time. The speed at which displacement changes is called velocity. Velocity is also a vector, because it includes both how fast something is moving and its direction. This is different from speed, which only tells you how fast something is moving, without caring about direction.
For example, a car driving at 60 km/h north has a velocity of 60 km/h north. A car driving at 60 km/h south has a different velocity, even though its speed is the same.
If you divide the total displacement by the time it took, you get the average velocity. This is also a vector. It's different from average speed, which is just the total distance traveled divided by the time.
How Does a Rigid Body Move?
When we talk about the movement of a rigid body (an object that doesn't change its shape, like a solid block), displacement can mean two things:
- Linear displacement: This is the straight-line movement of the entire body from one place to another. Imagine sliding a block across a table.
- Angular displacement: This describes how much the body has rotated around an axis. Imagine spinning a top or turning a door handle.
What Are Derivatives?
In physics, we often look at how things change over time. When we talk about how displacement changes, we use terms like velocity and acceleration. These are called "derivatives" of displacement.
Velocity
Velocity is how fast an object's displacement changes. It tells you both the speed and the direction of movement.
- If you know an object's displacement over time, you can find its velocity.
Acceleration
Acceleration is how fast an object's velocity changes. This means an object is accelerating if it's speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
- If you know an object's velocity over time, you can find its acceleration.
Jerk
Jerk is how fast an object's acceleration changes. This is less commonly used in everyday physics but is important in some advanced studies, like designing smooth rides for roller coasters.
See also

- Desplazamiento (vector) para niños (Displacement (vector) for kids - in Spanish)
- Position vector
- Motion vector