Displacement vector facts for kids
A displacement vector is a special idea in mathematics and physics. It's like an arrow that shows you two things: how far something has moved and in what direction. Think of it as the shortest, straight line path from where an object started to where it ended up.
Scientists use displacement vectors to understand how things move. For example, they help describe an object's speed and how its movement changes, which is called acceleration. It's all about finding the direct path between two points.
Contents
What is a Vector?
To understand displacement, it helps to know what a vector is. A vector is a quantity that has both a size (or "magnitude") and a direction.
- Magnitude: This is the "how much" part. For a displacement vector, it's the straight-line distance traveled.
- Direction: This is the "which way" part. It tells you if something moved north, south, up, down, or any other specific direction.
Things like speed, force, and acceleration are also vectors because they have both size and direction.
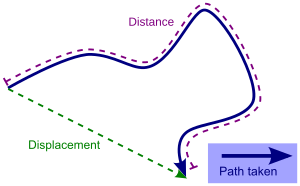
Displacement vs. Distance
It's easy to confuse displacement with distance, but they are different!
- Distance is the total length of the path an object travels. It doesn't care about direction. If you walk around a block, the distance you walked is the length of all four sides.
- Displacement is only the straight-line distance and direction from your starting point to your ending point. If you walk around a block and end up back where you started, your total distance might be long, but your displacement is zero! This is because you are back at your starting position.
Example of Displacement
Let's look at an example to make this clearer:
- Imagine your friend Tom walks 6 kilometres north from his home. His displacement from home is 6 km north. This is the straight line from his home to his current spot.
- Next, Tom walks 10 km south from that new spot.
- Now, let's figure out his total distance and displacement.
- The total distance Tom walked is 6 km + 10 km = 16 km. He covered a lot of ground!
- But what about his displacement from home? He went 6 km north, then 10 km south. This means he ended up 4 km south of his home (10 km south - 6 km north = 4 km south).
- So, his displacement from home is 4 km south. Even though he walked 16 km, the shortest path from his home to where he is now is just 4 km south.
Displacement helps us understand the net change in position, not just how much ground was covered.
How Displacement is Used
Displacement vectors are super important in physics and engineering.
- Navigation: They help ships, planes, and even GPS systems figure out the most direct route from one place to another.
- Sports: Coaches might use displacement to analyze an athlete's movement on a field, like how far a soccer player moved from their starting position during a play.
- Robotics: Robots use displacement calculations to move precisely from one point to another.
Understanding displacement helps us describe and predict how things move in the real world.
See also
 In Spanish: Desplazamiento (vector) para niños
In Spanish: Desplazamiento (vector) para niños