Electrocardiogram facts for kids
An electrocardiogram (say "ee-lek-tro-KAR-dee-oh-gram"), often called an ECG or EKG, is a special test. It records the electrical signals that make your heart beat. Think of it like listening to your heart's electrical song!
Each time your heart beats, tiny electrical impulses are sent out. An ECG machine records these signals as they travel through your heart. Doctors can then look at these recordings to understand how well your heart is working.
What is an Electrocardiogram?
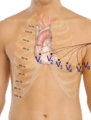
This test was invented by a scientist named Willem Einthoven. To do an ECG, small sticky pads called electrodes are placed on your skin. These are usually put on your chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to a machine that records the electrical activity of your heart. It's a quick and painless test!
Why Do Doctors Use ECGs?
Doctors use an ECG to check on your heart's health. It helps them see many things, such as:
- The speed and steadiness of your heartbeat.
- The size and position of your heart's chambers.
- If there's any damage to your heart.
- How medicines or devices like a artificial pacemaker are affecting your heart.
The ECG helps doctors find patterns in your heartbeats and rhythms. This helps them figure out if you have any heart conditions. You usually get the results of your ECG on the same day you have the test.
Images for kids
-
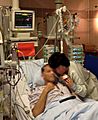
Use of real time monitoring of the heart in an intensive care unit in a German hospital (2015), the monitoring screen above the patient displaying an electrocardiogram and various values of parameters of the heart like heart rate and blood pressure
See also
 In Spanish: Electrocardiograma para niños
In Spanish: Electrocardiograma para niños