Electric stove facts for kids
An electric stove or electric range is a kitchen appliance that uses electricity to cook food. It has special parts called heating elements that get hot. People started using electric stoves because they were easier than old stoves that burned wood or coal. Some newer electric stoves even have a fan built in to remove smoke and smells.
The "burners" on an electric stove are the heating elements. You can control how hot they get. Some stoves have switches with set numbers, like 1 to 10, or settings like Low, Medium, and High. Other stoves have "infinite switches" that let you choose any heat level between low and high. Some burners even have thermostats to keep the temperature steady.
Contents
History of Electric Stoves
Early Ideas and Inventions
The idea for electric heating goes back a long way. On September 20, 1859, an inventor named George B. Simpson received a patent for an "electro-heater." He imagined it could warm rooms, boil water, and cook food.
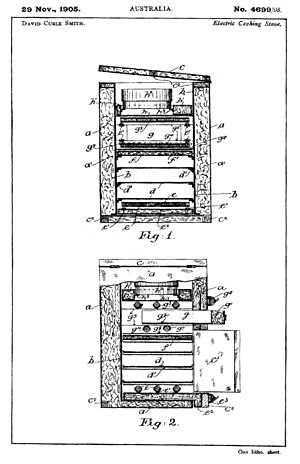
A Canadian inventor, Thomas Ahearn, filed a patent in 1892 for an "Electric Oven." He likely used it to cook a meal for a hotel in Ottawa that same year. The electric stove was shown off at the Chicago World's Fair in 1893. However, it took a while for electric stoves to become popular. This was partly because the technology was new. Also, many cities and towns did not yet have electricity.
In 1897, William Hadaway was granted a patent for an "Automatically Controlled Electric Oven." This was an important step for making ovens easier to use.
The Kalgoorlie Stove
In November 1905, David Curle Smith, an electrical engineer in Kalgoorlie, Australia, applied for a patent. He designed an electric stove that looked like gas stoves. It had an oven at the bottom, a hotplate on top, and a grill in between. This design became common for many electric stoves.
Curle Smith's stove did not have a thermostat. Instead, you controlled the heat by switching on different heating elements. There were nine elements in total.
After the patent was approved in 1906, manufacturing of the "Kalgoorlie Stove" began. The local electricity company bought all the stoves made. They rented them out to people living in Kalgoorlie. About 50 stoves were produced. This was the first time electric stoves were made for everyday households. Sadly, none of these original stoves still exist today. Many were melted down for their copper during World War I.
To help promote the stove, David Curle Smith's wife, H. Nora Curle Smith, wrote a cookbook. It was called Thermo-Electrical Cooking Made Easy and came out in March 1907. This was the world's first cookbook specifically for electric stoves. It included cooking instructions and 161 recipes.
Electric Stoves Become Popular
Three companies in the United States started selling electric stoves in 1908. But sales were slow at first. Early electric stoves had some problems. Electricity was expensive compared to wood or coal. The power supply was often limited. Also, it was hard to control the temperature, and the heating elements did not last long.
The invention of nichrome alloy helped a lot. Nichrome is a special wire that improved how long heating elements lasted and made them cheaper. Even so, electric stoves were still seen as new and unusual in the 1920s.
By the 1930s, the technology had gotten much better. The cost of electricity also went down. Electric stoves started to look more modern and stylish. This made them much more popular. Slowly, electric stoves began to replace gas stoves in many homes. Electric companies even promoted electric stoves to encourage more people to use electricity.
Types of Electric Stoves
Early electric stoves used heating coils that warmed up iron hotplates. You would place your pots on these hotplates. Later, new heating elements were made. These had resistive wires inside hollow metal tubes. These tubes were shaped like spirals and held the cookware directly.
In the 1970s, glass-ceramic cooktops started to appear. These cooktops have a smooth, flat surface. Glass-ceramic does not conduct heat very well, but it lets infrared light pass through easily. Electric heating coils or special halogen lamps underneath the glass heat up the surface.
A third type of electric stove is the induction stove. This also has a smooth glass-ceramic surface. However, induction stoves work differently. They use electromagnetic induction to heat only the pot itself, not the cooktop. This means only special pots and pans made of magnetic materials will work on an induction stove.
Electricity Use
A single heating element on an electric stove typically uses between 1 and 3 kilowatts of electricity. This depends on its size.
See also
 In Spanish: Cocina eléctrica para niños
In Spanish: Cocina eléctrica para niños