Emirate of Beihan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Emirate of Beihan
إمارة بيحان
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of the Federation of South Arabia | |||||||||
| 1680–1967 | |||||||||
|
Flag
|
|||||||||
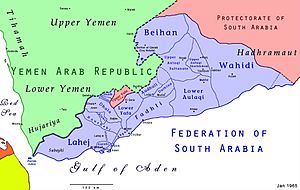 Map of the Federation of South Arabia |
|||||||||
| Capital | Suq Abdulla, (now Beihan) | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| • Coordinates | 13°25′N 45°40′E / 13.417°N 45.667°E | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
|
• 1946
|
6,000 | ||||||||
| • Type | Monarchy | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
|
• Documented since
|
1680 | ||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
1967 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
Beihan or Bayhan (Arabic: بيحان Bayḥān), officially known as the Emirate of Beihan (Arabic: إمارة بيحان Imārat Bayḥān), was a small state in the British Aden Protectorate. It later joined a group of states called the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital city was Suq Abdulla, which is now known as Beihan. The Emirate stopped being a separate state in 1967. It became part of the new People's Republic of South Yemen, and today it is part of the Republic of Yemen.
Contents
History of Beihan
The British government didn't get involved much with Beihan until they needed to draw clear borders for its northeastern area.
Early Agreements
In December 1903, a leader named Sharif Ahmed bin Muhsin signed an agreement, or treaty, with the British. This agreement also included the Ahl Masabein tribe. Sharif Ahmed bin Muhsin received a monthly payment of 30 dollars from the British.
Border Conflicts
In June 1930, soldiers from the Imam of Sanaa (a ruler from a nearby region) moved into the Harib district, which is north-west of Beihan. They started to move into Al Ain, an area where the Masabi tribesmen lived.
In 1955, Beihan signed a border treaty with North Yemen. This helped to settle where their shared border was. The Emirate of Beihan officially ended in 1967.
Geography of Beihan
Beihan is located north of the Beidha district and north-west of the Upper Aulaqi region. It sits on both sides of the Wadi Beihan, which is a valley. Most of the people in Beihan live in this valley.
Valley and Tribes
The lower part of the Wadi Beihan is home to the Sharif and his relatives, along with the Bal Harith tribe. The upper part of the valley is where the Ahl Masabein live. They are a strong tribe and make up most of the fighting men in Beihan.
The main base for the Sharif is at An Nuqub. The Bal Harith tribe's base is at As Seilan, and the Masabein's base is at Beihan al Qasab.
Fertile Land and Economy
Beihan is a fertile valley that connects Al Bayda in the north-west, Ma'rib in the east, and Ataq in the south. It gets water from streams flowing down from the northern mountains and from dug wells.
Farmers in Beihan grow dates, grains, and citrus fruits. Many people also raise livestock like sheep and goats to make a living. More and more people are also getting involved in trade and working for the government.
People of Beihan
Historically, the Bayhan valley had several main groups of people.
Southern Tribes
The Musabein Tribe lived in the south. This tribe was mainly led by two groups: Al-Saleh (from the Ahmed Saif tribe) and Alfatima (from the Naji Alawi tribe). These two groups often had conflicts with each other.
Central Valley Family
In the middle of the valley lived the Al-Habieli family. They are descendants of the Prophet. They arrived in the valley in the late 1600s. The Imam of Yemen had sent them to protect the important trade routes.
The Al-Habieli family are direct descendants of important religious leaders from Sana'a, the first being al Hadi Yahya bin Hussein and the seventh being Qassim al Mansur bin Abdullah.
Northern Tribes
The north of the valley was controlled by the Balharith Tribe. They also had their own conflicts about who should be their main leader. Like the Masabin, the Balharith tribe was also split into two main branches.
In 1931, it was estimated that about 11,000 people lived in Beihan.
Rulers of Beihan
The ruling family of Beihan was the Al-Habieli family. They were recognized by the Hashimite Grand Sharifs of Mecca as being related to them. The Al-Habieli family became religious leaders in Bayhan in 1680 and then became independent rulers.
The Hashemite Emirate of Bayhan was part of the Western Aden Protectorate. It later joined the Federation of Arab Emirates of the South in 1959 and then the Federation of South Arabia in 1962. The Emirate was ended by a revolution in Yemen in July 1967. The capital city was Naqub.
The current head of the Al-Habieli family is Al Amir (Prince) Khalid Saleh Hussein Al-Habieli.
Emirs of Beihan
Here are some of the past rulers, known as Emirs:
- Muqbil, the first Amir of Bayhan, started ruling around 1680.
- Emir Hasan
- Emir Ghaib, ruled from about 1750 to 1800.
- Emir Hussein, ruled from about 1800 to 1820.
- Emir al Habieli
- Emir Thaifallah
- Emir Mubarak
- Emir Muhsin, ruled until 1903. He became independent around 1900.
- Sharif Emir Ahmad Muhsin Al Habieli, Amir of Bayhan, ruled from 1903 until he stepped down in 1935. He was the father of:
- Sharif Sultan Hussein Ahmad Al Habieli, who was the Regent (a temporary ruler) of the Hashemite Emirate of Bayhan from 1935 to 1967. He was also the Minister of Interior for the Federation of South Arabia. Sharif Hussein was married to Halima, who was the daughter of the Sheikh of the Musabein tribe. Their son was:
- HH Sharif Emir Saleh Bin Hussein Al Habieli (1935-February 2010), who was the Emir of Bayhan. He lost his ruling powers on August 28, 1967, due to the revolution in Yemen.
- Prince Khalid Bin Saleh Bin Hussein Al-Habieli is the current Prince, starting from February 2010.
See also
- Aden Protectorate
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties


