T2 phage facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Enterobacteria phage T2 |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Virus classification | |
| Group: |
Group I (dsDNA)
|
| Order: |
Caudovirales
|
| Family: |
Myoviridae
|
| Genus: |
T4-like viruses
|
| Species: |
Enterobacteria phage T2
|
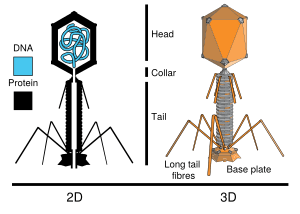
The T2 phage, also known as Enterobacteria phage T2, is a special kind of virus. It's a "bacteriophage," which means it infects and multiplies inside bacteria. Specifically, it attacks a common type of bacteria called Escherichia coli (often shortened to E. coli).
This tiny virus has a simple structure. It contains its genetic material, which is a long, linear piece of DNA. This DNA is protected by a strong outer shell made of protein. T2 phage is also known as a "tailed phage" because it has a distinctive tail-like structure. It belongs to a group of similar viruses called "T4-like viruses."
How T2 Phage Works
When a T2 phage finds an E. coli bacterium, it attaches itself to the outside. Then, it injects its DNA directly into the bacterial cell. This is a very clever trick! Most of the virus's protein shell stays outside the bacterium.
Once inside, the phage's DNA takes over the E. coli cell. It quickly turns the bacterium into a factory that only makes more T2 phages. The cell starts producing new viral DNA and proteins. Soon, many new phages are assembled inside the bacterium.
After the new phages are ready, they cause the E. coli cell to break open, or "rupture." This releases all the new T2 phages, which then go on to infect other bacteria. It's a very effective way for the virus to spread.
The Big Discovery: DNA's Role
The T2 phage played a very important role in science. In 1952, two scientists named Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase did famous experiments using this virus. Their work is known as the Hershey–Chase experiment.
They wanted to find out what carries genetic information: was it DNA or protein? By studying how T2 phage infected bacteria, they showed that it was the DNA, not the protein, that entered the bacterial cell. This injected DNA then directed the cell to make new viruses.
Their discoveries proved that DNA is the material that carries hereditary information. This means DNA tells living things how to grow, develop, and what traits they will have. This was a huge breakthrough in understanding genetics!
See also
 In Spanish: Fago T2 para niños
In Spanish: Fago T2 para niños

