Marrawah gum facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Marrawah gum |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Eucalyptus ovata in Maranoa Gardens | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eucalyptus |
| Species: |
E. ovata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eucalyptus ovata Labill.
|
|
 |
|
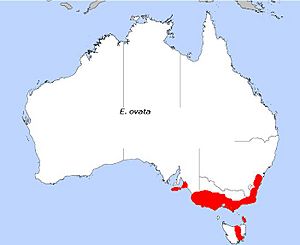
| E. ovata, field distribution | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Eucalyptus muelleri Naudin nom. illeg. |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Swamp Gum, also known as Black Gum, is a tree called Eucalyptus ovata. It's a small to medium-sized tree that only grows naturally in south-eastern Australia. This tree usually has smooth bark. Its adult leaves are shiny green and shaped like a spear or an egg. The flowers are white, and the buds are green, growing in groups of seven. After flowering, it produces fruit shaped like a cone or a bell.
Contents
What the Swamp Gum Looks Like
Eucalyptus ovata is a tree that typically grows to be about 17 to 30 meters (56 to 98 feet) tall. It can grow in different ways. Sometimes it's a bit straggly, but in other places, it has a strong, thick trunk.
This tree has smooth bark that can be grey, whitish, or pinkish-grey when it's new. On older, larger trees, you might find some rough, loose bark near the bottom.
Leaves and Buds
Young Swamp Gum plants and new shoots (called coppice regrowth) have leaves that are oval or egg-shaped. These leaves are usually 30 to 85 millimeters (1.2 to 3.3 inches) long and 25 to 60 millimeters (1 to 2.4 inches) wide.
Adult leaves are shiny green on both sides. They are shaped like a spear or an egg, measuring 80 to 180 millimeters (3.1 to 7.1 inches) long and 16 to 50 millimeters (0.6 to 2 inches) wide. They narrow down to a stalk called a petiole, which is 15 to 33 millimeters (0.6 to 1.3 inches) long.
The flower buds grow in the leaf axils (the angle between a leaf and the stem). They are on a stalk called a peduncle, which is 3 to 14 millimeters (0.1 to 0.6 inches) long. Each individual bud has its own tiny stalk, a pedicel, about 2 to 4 millimeters (0.08 to 0.16 inches) long.
When the buds are ready, they look like diamonds. They are 5 to 9 millimeters (0.2 to 0.4 inches) long and 4 to 6 millimeters (0.16 to 0.24 inches) wide. The top part of the bud, which covers the flower, is shaped like a cone and is called an operculum.
Flowers and Fruit
Swamp Gums mostly flower from June to November, and their flowers are white.
After the flowers, the tree produces a woody fruit. This fruit is a capsule (a dry fruit that opens to release seeds). It's shaped like a cone or a slightly bell-shaped cup. The capsule is 3 to 8 millimeters (0.1 to 0.3 inches) long and 4 to 8 millimeters (0.16 to 0.3 inches) wide. The parts that open to release the seeds are usually close to the rim of the fruit.
Naming the Swamp Gum
The scientific name Eucalyptus ovata was first officially described in 1806 by a scientist named Jacques Labillardière. He wrote about it in his book Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen.
The second part of the name, ovata, comes from the Latin word ovatus. This word means "egg-shaped," which refers to the shape of the tree's leaves.
In 1916, another scientist, Joseph Maiden, described two different types (or varieties) of E. ovata. These varieties are still recognized today:
- Eucalyptus ovata var. grandiflora Maiden;
- Eucalyptus ovata Labill. var. ovata.
Where the Swamp Gum Lives
The Swamp Gum is found in many places across south-eastern Australia. You can see it from the western part of Kangaroo Island and the southern Mount Lofty ranges in South Australia. It also grows in Tasmania, the southern half of Victoria, and in south-eastern New South Wales, as far north as Oberon and Hill Top.
These trees like to grow in grassy woodlands. They prefer places that are low-lying and can be wet for some time, or even permanently damp.
See also
 In Spanish: Eucalyptus ovata para niños
In Spanish: Eucalyptus ovata para niños
 | Aurelia Browder |
 | Nannie Helen Burroughs |
 | Michelle Alexander |

