Euler-Bernoulli Beam Theory facts for kids
The Euler–Bernoulli beam theory is a simple way to figure out how much a long, strong piece of material, called a beam, will bend when you put weight on it. It's also known as the engineer's beam theory or classical beam theory.
This theory works best for small bends. It doesn't look at how the beam might change shape from forces that try to slice it (called shear deformations).
Scientists first came up with this idea around 1750. It became very popular in the late 1800s. This was when famous structures like the Eiffel Tower and the Ferris wheel were being built.
Since then, engineers have used this theory in many areas. This includes designing machines and building structures. Even though newer, more complex methods exist, the Euler-Bernoulli beam theory is still used a lot. This is because it is easy to understand and use.
History of the Beam Theory
Two smart people, Leonhard Euler and Daniel Bernoulli, first put this theory together in 1750. Back then, science and engineering were seen differently than they are today. Many people didn't trust mathematical theories like this one for real-world building projects.
For a long time, bridges and buildings were designed using older methods. But in the late 1800s, things changed. The successful building of the Eiffel Tower and the Ferris wheel showed that the Euler-Bernoulli beam theory really worked. It proved its value on a very large scale.
How Beams Bend
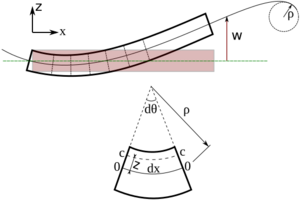
The Euler–Bernoulli theory helps engineers understand how a beam bends when a force pushes on it. Imagine a long, flat ruler. If you push down on the middle, it bends. The theory helps predict exactly how much it will bend.
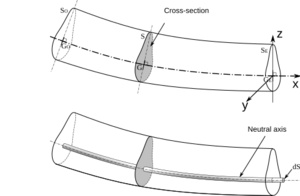
The main idea is that when a beam bends, its cross-sections (if you were to slice it) stay flat and at a right angle to the middle line of the beam. This middle line is called the "neutral axis." It's the part of the beam that doesn't stretch or squeeze when the beam bends.
Engineers use this theory to make sure that bridges, buildings, and other structures are strong enough. They can calculate how much a beam will bend under a certain weight. This helps them choose the right materials and shapes to keep everything safe.