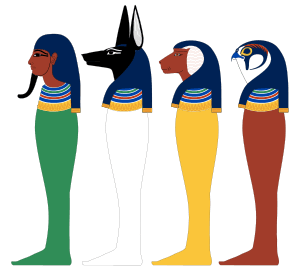Four sons of Horus facts for kids
The Four Sons of Horus were important gods in ancient Egyptian religion. They were believed to protect the organs of people who had died. These gods were often shown as the lids of special jars called canopic jars. Each jar held a different organ from the deceased.
Contents
Who Were the Four Sons of Horus?
The Four Sons of Horus were a group of four gods. They were thought to be the children of the god Horus, or sometimes the god Osiris. Their main job was to guard the internal organs of the dead. This was a very important part of the mummification process.
Their Role in Mummification
When ancient Egyptians prepared a body for the afterlife, they removed the internal organs. These organs were then preserved and placed into four special jars. These jars are known as canopic jars. Each of the Four Sons of Horus protected one specific organ.
- Imsety had a human head. He was the guardian of the liver.
- Duamutef had the head of a jackal. He protected the stomach.
- Hapi had the head of a baboon. He was the protector of the lungs.
- Qebehsenuef had the head of a falcon. He guarded the intestines.
The heart was usually left inside the body. The brain was removed but not preserved in a jar.
Why Were They Important?
The ancient Egyptians believed that to have a successful afterlife, the body needed to be preserved. This included the organs. The Four Sons of Horus made sure these organs were safe. They helped the deceased person reach the afterlife safely. They were often shown on coffins and tombs.
Images for kids
-
The heads of the "Four Sons of Horus" used as canopic jar stoppers, on display at the British Museum.