Frequency response facts for kids
When you listen to music, you hear many different sounds, from deep bass to high-pitched treble. A frequency response graph helps us understand how well a system, like a speaker or a microphone, handles these different sounds. It shows if the system makes some sounds louder (amplifies them) or quieter (attenuates them) compared to others. Think of it like a report card for sound, showing how a device performs across the entire range of sounds.
This idea is super important for things that deal with sound, like loudspeakers, headphones, and even audio crossovers, which are devices that split sound signals into different frequency ranges for speakers.
Contents
Understanding Frequency Response
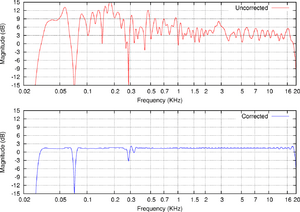
Frequency response is usually shown as a graph. This graph plots how loud a sound is (the output) compared to how loud it was originally (the input), for different sound frequencies.
What are Frequencies?
Sound travels in waves, and the "frequency" of a sound wave tells us how many waves pass by in one second. This is measured in Hertz (Hz).
- A low frequency, like 20 Hz, means a very deep bass sound.
- A high frequency, like 20,000 Hz (or 20 kHz), means a very high-pitched sound.
- Humans can usually hear sounds from about 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
How Frequency Response is Described
When you look at the specifications for a speaker or headphones, you might see a frequency response listed as two numbers, for example, "20 Hz - 20,000 Hz."
- The first number (e.g., 20 Hz) tells you the lowest bass frequency the product can produce.
- The second number (e.g., 20,000 Hz) tells you the highest high-frequency it can produce.
A wider range, like 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, generally means the device can reproduce a full range of sounds that humans can hear. However, the graph itself shows how evenly it produces those sounds. A "flat" frequency response means the device plays all frequencies at roughly the same loudness, which is often considered ideal for accurate sound.
Where is Frequency Response Used?
Frequency response is a key concept in many areas of technology and science.
In Audio Equipment
- Loudspeakers and Headphones: This is where you'll most often hear about frequency response. A good speaker aims for a flat frequency response so that music sounds natural, without some instruments being too loud or too quiet.
- Microphones: Microphones also have a frequency response, showing how well they pick up different pitches of sound. Some microphones are designed to pick up voices clearly, while others are better for musical instruments.
- Audio Crossovers: These devices separate audio signals into different frequency bands (like bass, midrange, and treble) and send them to the right speaker drivers (woofers, mid-range speakers, tweeters). Their frequency response shows exactly how they split these sounds.
Beyond Audio
The idea of frequency response isn't just for sound! It's used in many other fields, like:
- Electronics: To see how electronic circuits handle different electrical signals.
- Control Systems: To understand how a system reacts to different speeds of change in its input.
- Medical Imaging: In technologies like MRI, understanding frequency response helps create clear images.
See also
 In Spanish: Respuesta en frecuencia para niños
In Spanish: Respuesta en frecuencia para niños