Loudspeaker facts for kids
A loudspeaker, or just a speaker, is a device that makes sound. You can find speakers in many places, like radios, television sets, and musical instrument amplifiers. Speakers change electrical signals into sounds that we can hear.
Contents
How Speakers Make Sound
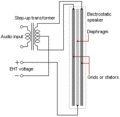
Speakers use both electricity and movement to create sound. First, an electrical signal comes from a radio, TV, or music player. This signal needs to be connected to an electronic amplifier to make it strong enough.
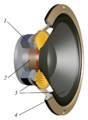
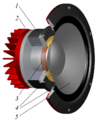
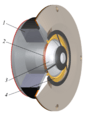
Most speakers have a few main parts:
These parts are often placed inside a wooden box. When the electrical signal goes through the copper wire coil, it creates a magnetic field. This field interacts with the main magnet. This causes the coil to move back and forth very quickly.
As the coil moves, it makes the paper cone vibrate. These vibrations push and pull the air around the cone, creating sound waves. These sound waves travel to our ears, and we hear the sound! Some speakers also have a special part called an audio crossover. This helps direct different sound frequencies to the right parts of the speaker.
Different Kinds of Speakers
Speakers come in different types, each designed for specific sounds.
Speakers for Low Sounds
Some speakers are made for deep, low-pitched sounds. These are called woofer loudspeakers or subwoofer loudspeakers. They are usually larger to move more air and create those deep bass notes.
Speakers for High Sounds
Other speakers are called tweeters. These are designed to make high-pitched sounds. Think of the sound of a whistle or a bird singing. Tweeters are often smaller.
Speakers for Instruments
Loudspeakers used for electric musical instruments are usually much stronger. They are also heavier than speakers for radios or TVs. Their main job is to turn the electrical signals from an instrument into loud, clear music.
The History of Speakers
The first speaker that could make sound was invented in 1876. Alexander Graham Bell created it. He needed a way to make sounds louder for his telephone invention.
Later, in 1878, a German inventor named Werner von Siemens made an even better speaker. His design was an improved type of electrodynamic loudspeaker. However, it still needed a separate amplifier to make the sound truly loud.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Altavoz para niños
In Spanish: Altavoz para niños