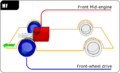
Front-wheel drive facts for kids
Front-wheel drive, often called FWD, is a type of car design. In FWD cars, the engine's power goes only to the front wheels. These front wheels then pull the car along.
FWD cars are usually good in wet or snowy weather. This is because the weight of the engine is over the front wheels. This extra weight helps the front wheels get better traction (or grip) on the road. This makes the car feel safer and more stable.
However, FWD cars can sometimes have an uneven weight distribution. This means more weight is at the front. While generally safe, this design has specific characteristics that engineers consider when designing the car's braking system.
Contents
How Front-Wheel Drive Works
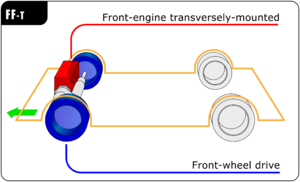
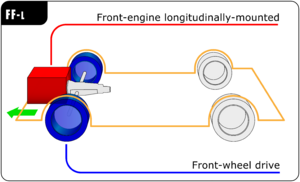
In a front-wheel drive car, the engine, transmission (which changes gears), and differential (which lets wheels spin at different speeds) are all usually placed at the front of the car. This setup is often called a "transaxle."
Engine Placement
Most FWD cars today have the engine placed sideways, or transversely. This saves space and makes the car more compact. Some older or larger FWD cars might have the engine placed lengthwise, or longitudinally.
Power to the Wheels
The power from the engine goes through the transmission to a special part called a drive shaft. This drive shaft connects to the front wheels using constant-velocity joints (often called CV joints). These joints are very important because they allow the wheels to turn and move up and down over bumps while still getting power smoothly.
History of Front-Wheel Drive
Front-wheel drive is not a new idea. Engineers have been experimenting with it for a long time.
Early Ideas
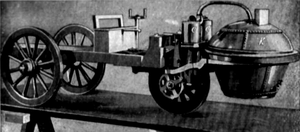
- In 1769, a French inventor named Nicholas Cugnot built a steam-powered vehicle. It was designed to pull cannons and had its power at the front wheels.
- In 1898, the Gräf car from Austria was one of the first cars with an engine at the front that also drove the front wheels.
- Around the same time, other inventors like Henry Sutton in England and Latil in France also worked on FWD designs.
Racing and Production Cars
- In the 1920s, some racing cars, like the 1925 Miller 122, used front-wheel drive. This design helped them handle better on the track.
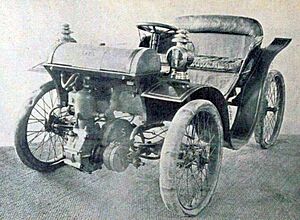
- The 1929 Cord L-29 was the first mass-produced FWD car in the United States. It was also one of the first cars in the world to use those important constant-velocity joints.
- The 1934 Citroën Traction Avant was a very famous FWD car from France. Its name even means "front-wheel drive." It was known for its modern design and good handling.
- In 1932, the German company Adler launched the Trumpf Junior, which became a very popular FWD car, selling over 100,000 units by 1939.
Modern FWD Cars
A big step for FWD cars was the 1959 Mini. This small British car used a clever design where the engine was placed sideways (transverse) and drove the front wheels. This made the car very compact and roomy inside for its size. This design became very popular and is now used in most small and medium-sized cars around the world.

Many car companies, like Renault, Fiat, Audi, and Subaru, have used and improved front-wheel drive designs over the years. Cars like the Fiat 128 and Chevrolet Cobalt are examples of popular FWD vehicles. Even some racing cars, like the Nissan GT-R LM Nismo, have explored FWD for performance.


Advantages of Front-Wheel Drive
- Better Traction: The weight of the engine over the front wheels helps them grip the road, especially in slippery conditions like rain or snow.
- More Interior Space: Since all the main parts (engine, transmission, differential) are at the front, there's no need for a drive shaft running to the back wheels. This leaves more room inside the car for passengers and cargo.
- Lower Cost: FWD cars are often simpler to build than cars with power going to all four wheels or just the back wheels. This can make them less expensive to buy and maintain.
- Better Fuel Economy: FWD systems are generally lighter and more efficient, which can lead to better gas mileage.
Disadvantages of Front-Wheel Drive
- Torque Steer: Sometimes, when a powerful FWD car accelerates quickly, the steering wheel might pull slightly to one side. This is called "torque steer."
- Weight Distribution: Having most of the weight at the front can affect how the car handles, especially during hard cornering or braking.
- Limited Towing: FWD cars are generally not as good at towing very heavy loads compared to rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tracción delantera para niños
In Spanish: Tracción delantera para niños
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |