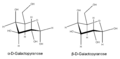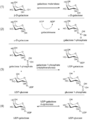Galactose facts for kids
Galactose (say: GAL-uh-tose) is a type of sugar. Its name comes from the Greek word for "milk." It is very similar to another common sugar called glucose. You won't find large amounts of pure galactose by itself in nature. Instead, it's usually found joined with glucose to make lactose. Lactose is the main sugar found in milk and other dairy products.
When you eat foods with lactose, your body digests it. This process breaks lactose into glucose and galactose. After being absorbed into your body, galactose travels to your liver. There, your liver changes it into either glucose (which your body uses for energy) or glycogen (which is stored energy).
Contents
What is Galactose?
Galactose is a simple sugar, also known as a monosaccharide. This means it's made of just one sugar unit. Its chemical formula is C6H12O6. Even though it has the same formula as glucose, its atoms are arranged a little differently. This small difference makes it a unique sugar.
Where Do We Find Galactose?
You mostly find galactose as part of lactose, the sugar in milk. This includes cow's milk, goat's milk, and even human breast milk. Because of this, galactose is an important part of the diet for babies and young children. It's also found in some fruits, vegetables, and fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir.
How Your Body Uses Galactose
After you eat lactose, special enzymes in your body break it down. One of these enzymes is called lactase. It splits lactose into glucose and galactose. Both of these simple sugars then enter your bloodstream.
Once in your liver, galactose is changed. Your liver has a special pathway, sometimes called the Leloir pathway, that turns galactose into glucose. Glucose is the main sugar your body uses for energy. If your body has enough energy, glucose can be stored as glycogen for later use.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Galactosa para niños
In Spanish: Galactosa para niños