Galvanic isolation facts for kids
Galvanic isolation is a clever way to keep different parts of an electrical circuit totally separate from each other. Think of it like building a fence between two areas to make sure nothing can directly pass through. In electronics, this means preventing an electric current from flowing directly between two circuits.
Why do we need this "fence"? It's mainly for safety and to stop electrical noise or interference from messing things up. For example, it can protect people from electric shocks or make sure sensitive electronic parts work correctly without being disturbed by other circuits.
There are a few common ways to achieve galvanic isolation. Some popular methods include using special devices like relays, opto-isolators, and transformers. Each of these acts like a barrier, allowing signals or power to transfer without a direct electrical connection.
Contents
What is Galvanic Isolation?
Galvanic isolation means there is no direct path for an electric current to flow between two circuits. Imagine two separate pools of water that can't mix, even if they are next to each other. In electronics, this separation is achieved using a non-conductive barrier.
This barrier stops unwanted currents, called "ground loops," from forming. Ground loops can cause buzzing sounds in audio equipment or errors in data signals. By breaking the direct electrical connection, galvanic isolation helps circuits work more reliably and safely.
Why is Isolation Important?
Galvanic isolation is super important for several reasons, especially in modern electronics. It helps keep people safe and makes sure devices work properly.
Protecting People from Shocks
One of the biggest reasons for galvanic isolation is safety. Imagine a device plugged into a wall outlet. If there's a fault, a high voltage could accidentally reach the parts a person might touch. Galvanic isolation creates a barrier that prevents this dangerous voltage from passing through. This is crucial in medical equipment, power supplies, and many household appliances. It ensures that even if one part of the circuit has a problem, the user remains safe from electric shock.
Preventing Electrical Noise
Electronic devices often produce electrical noise, which can interfere with other circuits. This noise can cause errors in data, make signals unclear, or even damage sensitive components. Galvanic isolation acts like a shield, blocking this noise from traveling between different parts of a system. For example, it's used in computers and communication networks to ensure clear and accurate data transfer.
Handling Different Voltages
Sometimes, different parts of a system need to operate at very different voltage levels. For instance, a small control circuit might use 5 volts, while a motor it controls needs 240 volts. Galvanic isolation allows these circuits to communicate without directly connecting their power supplies. This protects the low-voltage circuit from the high voltage, preventing damage and ensuring stable operation.
How is Isolation Achieved?
Several electronic components are designed specifically to provide galvanic isolation. They transfer signals or power without a direct electrical connection.
Using Transformers
Transformers are one of the oldest and most common ways to achieve galvanic isolation. A transformer has two coils of wire, called the primary and secondary coils. These coils are not physically connected. Instead, they are wound around a shared magnetic core.
When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces a current in the secondary coil. Because there's no direct electrical link between the coils, the input and output circuits are galvanically isolated. Transformers are often used in power supplies to step down voltage safely and provide isolation.
Using Opto-isolators
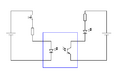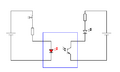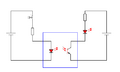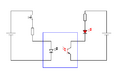
An opto-isolator, also known as an optocoupler, uses light to transfer signals. It has a light-emitting diode (LED) on one side and a light-sensitive sensor (like a phototransistor) on the other.
When an electrical signal goes into the LED, the LED lights up. The light then shines on the sensor, which turns the light back into an electrical signal. Since the only connection between the input and output is light, there's no direct electrical path. This makes opto-isolators excellent for isolating digital signals in sensitive circuits, like those found in computers or industrial control systems.
Using Relays
A relay is an electrical switch that uses an electromagnet to open or close another circuit. It has two main parts: a coil and a set of electrical contacts.
When current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that pulls a metal arm, causing the contacts to either connect or disconnect. The control circuit (which powers the coil) is completely separate from the circuit being switched by the contacts. This physical separation provides galvanic isolation. Relays are often used to control high-power circuits with low-power signals, protecting the control circuit from high voltages or currents.
Where is Galvanic Isolation Used?
Galvanic isolation is used in many places you might not even realize, making our electronic world safer and more reliable.
Medical Devices
In hospitals, medical equipment like ECG machines or patient monitors must be extremely safe. Galvanic isolation is critical here to protect patients from electric shocks. It ensures that even if there's a fault in the power supply, no dangerous current can reach the patient.
Industrial Control Systems
Factories and industrial plants use complex machinery controlled by computers. These environments can be very noisy electrically. Galvanic isolation protects sensitive control circuits from high voltages and electrical interference coming from motors, pumps, and other heavy machinery. This helps prevent errors and ensures the machines operate smoothly.
Communication Networks
When you use the internet or make a phone call, data travels through many devices. Galvanic isolation is used in ethernet connections and other communication systems to prevent electrical noise from corrupting data signals. It ensures that information is transmitted clearly and accurately between devices, even if they are in different buildings or have different power sources.
Electric Vehicles
Electric cars and bikes use high-voltage batteries and powerful motors. Galvanic isolation is essential in these vehicles to separate the high-voltage power systems from the low-voltage control electronics and the parts a driver might touch. This design keeps both the vehicle's systems and its occupants safe.
Images for kids
-
An opto-isolator is a very popular method of isolation in digital circuits.
-
Everlight EL817 phototransistor opto-isolator in DIP-4 package
-
Halo TG110-S050N2RL 10/100Base-TX ethernet pulse transformer in SO-16 package
See also
 In Spanish: Aislamiento galvánico para niños
In Spanish: Aislamiento galvánico para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |