Gas chromatography facts for kids
Imagine you have a mix of different smells, like a perfume. How would you separate them? Gas chromatography is a clever science trick that does just that! It's a way to separate and identify different parts of a gas mixture. First, the stuff you want to test is turned into a gas. Then, a special gas, like helium, pushes it through a long, thin tube called a column. As the mixture travels, its parts separate. This happens inside a hot oven, which helps each part come out at a different time.
Contents
How a Gas Chromatograph Works
A gas chromatograph is the machine used for this separation. It has a few main parts that work together to get the job done.
The Carrier Gas
The carrier gas is like the delivery truck for your sample. It's a gas that doesn't react with anything in your sample, like helium or nitrogen. This gas pushes your sample through the machine.
Why the Right Gas Matters
Choosing the right carrier gas is important. It needs to be a gas that won't mix or react with your sample. It also needs to handle the heat from the oven.
Gas Flow Speed
The speed of the carrier gas also matters. If it's too fast, your sample won't have enough time to separate properly. If it's too slow, the whole experiment will take a very long time.
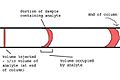
The Separation Column
The column is the heart of the separation process. It's a very long, thin tube, usually coiled up to fit inside the oven. Most columns are made of special glass or metal.
How the Column Separates
Inside the column, there's a special coating or material. As your gas sample travels through, different parts of the sample stick to this material for different amounts of time. Think of it like a race where some runners get stuck in mud for longer than others. This sticking and unsticking is what separates the mixture into its individual parts.
Types of Columns
The most common type is a capillary column. These are very thin tubes. Some have a thin layer of a special liquid on the inside wall. Others have a thin film of support material. Both types help separate the sample as it moves through.
The Oven's Role
The column sits inside a special oven. This oven's job is to keep a very steady temperature.
Temperature Control
The temperature of the oven is super important. It needs to be set just right, usually a bit hotter than the boiling point of your sample. This helps the sample stay as a gas and move through the column.
Heating Programs
If your sample has many parts that boil at very different temperatures, the oven can use a "temperature program." This means the oven slowly gets hotter during the experiment. Higher temperatures make parts move faster through the column. Lower temperatures make them move slower, but you get a clearer separation.
The Detector
After the sample leaves the column, it goes to a detector. The detector's job is to "see" each separated part as it comes out and send a signal.
Flame Ionization Detector (FID)
One common detector is the flame ionization detector. Here, the separated gas from the column is burned in a small flame. When the gas burns, it creates tiny charged particles called ions. These ions are then counted, which tells you how much of that part of the sample was there. This detector can't see water, carbon dioxide, or some other simple gases.
Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD)
Another type is the thermal conductivity detector. This detector has an electrically heated wire. When a separated part of your sample passes over the wire, it changes how well the wire conducts heat. The detector measures this change in heat, which tells it that a part of your sample has arrived. This detector can see almost all types of compounds.
Mass Spectrometry Detector (MSD)
A mass spectrometry detector is very powerful. It can not only detect the separated parts but also figure out what they are! It breaks the sample into tiny pieces and then measures their weight. This helps scientists identify exactly what chemicals were in the original mixture.
Types of Mass Spectrometers
Two common types are quadrupole and time-of-flight mass analyzers. A quadrupole uses electric fields to sort ions by their weight. A time-of-flight measures how fast ions travel, which also tells you their weight.
What Gas Chromatography is Used For
Gas chromatography is used all the time to figure out what's inside a complex mixture.
Identifying Substances
When the separated parts come out of the column, the detector creates a graph. This graph shows when each part came out and how much of it there was. By looking at these graphs, scientists can identify the different chemicals in the original sample.
Checking Quality
This method is super useful for checking the quality of products. For example, it can be used to:
- Make sure medicines have the right ingredients.
- Check the quality of drinks.
- Ensure perfumes have the correct scent chemicals.
- Test for pollutants in air or water.
By comparing a sample to a known standard, scientists can tell exactly how much of each part is present.
Images for kids
-
This image above shows the interior of a GeoStrata Technologies Eclipse Gas Chromatograph that runs continuously in three-minute cycles. Two valves are used to switch the test gas into the sample loop. After filling the sample loop with test gas, the valves are switched again applying carrier gas pressure to the sample loop and forcing the sample through the column for separation.
See also
 In Spanish: Cromatografía de gases para niños
In Spanish: Cromatografía de gases para niños