Haplogroup facts for kids
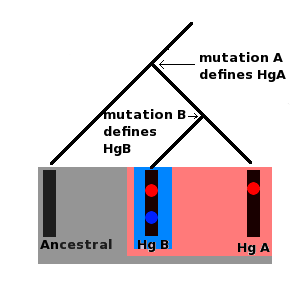
A haplogroup is like a special family group for your DNA. It's a group of people who share a common ancestor from many, many years ago. They all have the same small change, called a mutation, in a specific part of their DNA.
These DNA changes help scientists trace human family trees back thousands of years. They show us how different groups of people are related.
Contents
Types of Haplogroups
In human studies, the most common haplogroups looked at are:
- Y-chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups: These are passed down only from a father to his sons.
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups: These are passed down only from a mother to all her children (both sons and daughters).
Because Y-DNA and mtDNA are passed down in these special ways, they don't mix up like other parts of our DNA. They only change by chance mutations. This makes them very useful for tracking ancient family lines and human migrations around the world.
How Haplogroups Help Us Learn About History
Haplogroups are like genetic markers that tell a story about our ancestors. By studying them, scientists can:
- Trace ancient migrations: They can see how early humans moved out of Africa and spread across the continents.
- Understand population history: They help us learn about how different groups of people settled in certain areas.
- Connect modern populations: They show how people living in different parts of the world today are linked by shared ancestry.
Related Pages
Images for kids
-
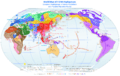
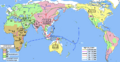
Map of human haplotype migration, according to mitochondrial DNA, with key (coloured) indicating periods in numbered thousands of years before the present.
See also
 In Spanish: Haplogrupo para niños
In Spanish: Haplogrupo para niños