Hazel Perfect facts for kids
Hazel Perfect (born around 1927, died July 8, 2015) was a smart British mathematician. She was an expert in a field of math called combinatorics. This area of math deals with counting, arranging, and combining things.
What She Achieved
Hazel Perfect made many important contributions to mathematics. She was known for:
- Inventing something called gammoids. These are special mathematical structures.
- Working with another mathematician, Leon Mirsky, on doubly stochastic matrices. These are types of number grids used in math.
- Writing three important math books: Topics in Geometry, Topics in Algebra, and Independence Theory in Combinatorics.
- Translating a math book by Pavel Alexandrov from German into English. The book was called An Introduction to the Theory of Groups.
The Perfect–Mirsky Conjecture
One of her famous works was the Perfect–Mirsky conjecture. This idea is named after Hazel Perfect and Leon Mirsky. It is about the eigenvalues of doubly stochastic matrices. Eigenvalues are special numbers linked to these matrices.
Perfect and Mirsky thought that for certain matrices (called 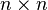 matrices), these eigenvalues would form a shape. They believed the shape would be a mix of regular polygons. These polygons would have their corners at special points called roots of unity.
matrices), these eigenvalues would form a shape. They believed the shape would be a mix of regular polygons. These polygons would have their corners at special points called roots of unity.
They proved their idea was true for small matrices (when 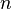 was 2 or 3). Later, it was also shown to be true for
was 2 or 3). Later, it was also shown to be true for  . However, it turned out to be false for
. However, it turned out to be false for  . For even larger values of
. For even larger values of 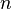 , mathematicians are still working to find the answer.
, mathematicians are still working to find the answer.
Her Life and Career
Hazel Perfect was a dedicated student and teacher.
- In 1949, she earned her master's degree from Westfield College. This was a college for women that was part of the University of London. Her master's paper was about how to simplify matrices.
- In the 1950s, she taught math at University College of Swansea. While there, she worked with Gordon Petersen to translate Alexandrov's math book.
- She continued her studies and earned her Ph.D. from the University of London in 1969. Her Ph.D. research focused on how things are connected in math, especially in graphs.
- Later in her career, she became a senior lecturer (called a reader) in mathematics at the University of Sheffield.
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |

