Coronary artery bypass surgery facts for kids
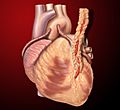
Coronary artery bypass surgery is a special type of surgery that helps people with heart disease. It helps stop chest pain that happens when the heart doesn't get enough blood. This surgery also lowers the chance of serious problems from heart disease.
Doctors often call it coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), which sounds like "cabbage." You might also hear it called heart bypass or just bypass surgery.
During this surgery, doctors take healthy blood vessels from another part of the patient's body. They then attach these new vessels to the heart. This creates a new path for blood to flow around any blocked blood vessels. It's like building a new road to go around a traffic jam! This way, more blood can reach the heart, helping it work better.
Sometimes, the heart is stopped during the surgery. When this happens, special machines take over the job of the heart and lungs. But it's also possible to do the surgery while the heart is still beating. This is called "off-pump" surgery.
How Many Surgeries Are Done?
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is a very common procedure in U.S. hospitals. In 2011, it made up about 1.4% of all surgeries done in operating rooms.
However, the number of these surgeries has gone down over time. Between 2001 and 2011, the number of CABG procedures dropped by 46%. In 2001, about 395,000 surgeries were performed. By 2011, this number was around 213,700.
History of Heart Bypass Surgery
The first coronary artery bypass surgery in the United States happened on May 2, 1960. It took place at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine-Bronx Municipal Hospital Center.
A team led by Robert H. Goetz performed this important surgery. He worked with thoracic surgeon Michael Rohman, and assistants Jordan Haller and Ronald Dee. This marked a big step forward in treating heart disease.
Images for kids
-
René Gerónimo Favaloro was an Argentine heart surgeon. He was famous for his early work on coronary artery bypass surgery. He used a vein from the leg called the great saphenous vein.
-
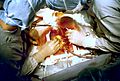
This picture shows coronary artery bypass surgery. Doctors are carefully moving the right coronary artery away from the yellow adipose tissue (fat). The tube at the bottom helps return blood from the heart-lung machine. The patient's heart is stopped during this part of the surgery.
See also
 In Spanish: Baipás coronario para niños
In Spanish: Baipás coronario para niños