Heat exchanger facts for kids
A heat exchanger is a clever device that helps move heat from one liquid or gas to another. Imagine you have something hot and something cold, and you want to make the cold thing warmer without mixing them together. That's exactly what a heat exchanger does! It's super useful in many everyday things, from keeping your house warm to making your fridge cold.
Contents
How Do They Work?
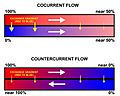
Heat exchangers work by allowing heat to flow from a warmer fluid to a cooler fluid. This usually happens across a solid wall, like a metal plate or tube, which keeps the two fluids separate. The heat energy naturally moves from the hotter side to the colder side until the temperatures become more balanced.
Keeping Fluids Separate
Most heat exchangers keep the fluids apart. This means the hot liquid doesn't mix with the cold liquid. Instead, the heat travels through a barrier, like a thin metal wall. This is important because sometimes the fluids are different, or you don't want them to get mixed up.
Where Do We Use Them?
Heat exchangers are all around us, even if we don't always see them!
- In your home: Your refrigerator uses a heat exchanger to remove heat from inside and keep your food cold. Your air conditioner also uses one to cool your home.
- In cars: The radiator in a car is a type of heat exchanger. It cools down the engine by transferring heat from the engine's hot coolant to the air.
- In power plants: Large heat exchangers are used to turn water into steam to generate electricity.
- In swimming pools: They can be used to heat pool water using a different heat source.
- In factories: Many industries use them to heat or cool products during manufacturing processes.
Different Types of Heat Exchangers
There are many kinds of heat exchangers, each designed for specific jobs. They might look different, but they all do the same basic thing: move heat! Some common types include:
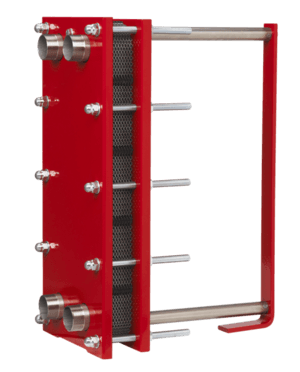
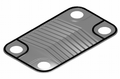
- Plate heat exchangers: These use many thin, wavy plates to create a large surface area for heat transfer. They are often used in heating systems and food processing.
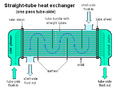
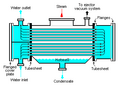
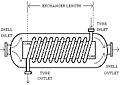
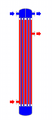
- Shell and tube heat exchangers: These have a bundle of tubes inside a large shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, and the other flows around the tubes inside the shell. They are very common in power plants and chemical factories.
- Double pipe heat exchangers: These are simpler, with one pipe inside another. One fluid flows through the inner pipe, and the other flows through the space between the two pipes.
Here are some other types you might hear about:
- Adiabatic wheel heat exchanger
- Dynamic scraped surface heat exchanger
- Fluid heat exchanger
- Phase-change heat exchanger
- Pillow plate heat exchanger
- Plate and shell heat exchanger
- Plate fin heat exchanger
- Waste Heat Recovery Unit heat exchanger
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Intercambiador de calor para niños
In Spanish: Intercambiador de calor para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |