The Holocaust facts for kids
The Holocaust was a terrible time when Nazi Germany and its helpers systematically murdered about six million Jewish people in Europe. This happened during World War II, between 1941 and 1945. This number was about two-thirds of all Jewish people living in Europe at that time. It is considered the largest genocide in human history.
The Nazis had a harmful belief system based on racism. They believed their race was superior and wanted more "living space" for Germans. When they took power in 1933, they started making laws against Jewish people. They also organized a violent attack across Germany in November 1938. After Germany invaded Poland in 1939, Nazis created special areas called ghettos. They forced Jewish people to live in these crowded, isolated places.
In June 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union. German forces and local helpers then killed between 1.5 and 2 million Jewish people by shooting them. Later, in 1941 or early 1942, the top German leaders decided to murder all Jewish people in Europe. This plan was called the "Final Solution".
Victims were sent by train to special extermination camps. If they survived the journey, most were killed using poison gas. Other Jewish people were forced to work in labor camps. Many died there from hunger, exhaustion, or from cruel medical experiments. It was very hard for Jewish people to escape or hide. They often lacked money to pay for help, and there was a high risk of being reported to the Nazis. The homes, jobs, and belongings of murdered Jewish people were taken by the Germans and others. Most victims died in 1942, but the killing continued until the war ended in May 1945.
After the war, many Jewish survivors moved out of Europe. Today, the Holocaust is remembered in museums and memorials. It is also shown in art and culture. It serves as a powerful reminder of extreme human evil.
How Many People Died?
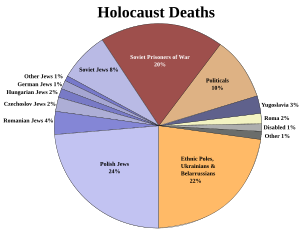
About six million Jewish people were killed during the Holocaust. Most of these victims were from Eastern Europe, with about half of them from Poland alone. Around 1.3 million Jewish people who lived under Nazi rule or in allied countries survived the war. This means that one-third of the world's Jewish population and two-thirds of Europe's Jewish population were killed.
The number of deaths varied greatly depending on the area. In some places, almost 100 percent of the Jewish population was killed. Some Jewish people survived because they could emigrate or were protected by Germany's allies. About 600,000 Jewish people were saved this way. Jewish children and older people had an even lower chance of surviving than adults.
The deadliest part of the Holocaust was called Operation Reinhard. During this time, special extermination camps were used. About two million Jewish people were killed between March 1942 and November 1943. In just 100 days, from late July to early November 1942, about 1.47 million Jewish people were murdered. This was a very fast rate of killing.
People Who Deny the Holocaust
Some people claim that the Holocaust did not happen, or that it was not as bad as historians say. This is called Holocaust denial. However, almost all historians agree that the Holocaust did happen exactly as described. People who deny the Holocaust sometimes say that the Nazis did not kill as many people as historians claim. Instead, they say many people died from diseases or lack of food, and that it was not the Nazis' fault.
In some countries in Europe, it is against the law to say that the Holocaust never happened.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Holocausto para niños
In Spanish: Holocausto para niños

