Homophone facts for kids
Homophones are words that sound exactly the same as another word, but they have different meanings. Often, they also have different spellings. Think of them like word twins that sound alike but are unique!
For example, the word "to" (meaning toward something) sounds just like "two" (the number) and "too" (meaning also or very). Even though they sound identical, you use them in very different ways.
Homophones can sometimes be tricky because you have to know the meaning from the way they are used in a sentence. They are a fun part of the English language!
Contents
What are Homophones?
Homophones come from two Greek words: "homo," meaning "same," and "phone," meaning "sound." So, literally, they are "same sounds."
When we talk, we often don't notice the difference between homophones because our brains understand the meaning from the rest of the sentence. But when you are writing, it's important to choose the correct spelling for the meaning you want to share.
Common Examples of Homophones
Let's look at some everyday examples of homophones. You probably use many of these all the time!
- fore, four: "The fore part of the boat" vs. "I have four apples."
- it's, its: "It's a sunny day" (meaning "it is") vs. "The dog wagged its tail."
- there, their, they're: "The book is over there" vs. "Their house is big" vs. "They're going to the park" (meaning "they are").
- Knight, night: "A brave knight rode a horse" vs. "It is dark at night."
- which, witch: "Which color do you like?" vs. "A scary witch."
- pore, poor, pour: "Skin has tiny pores" vs. "A poor person" vs. "Please pour the water."
- pear, pair, pare: "Eat a juicy pear" vs. "A pair of shoes" vs. "Pare the apple skin."
- see, sea, C: "I can see the ocean" vs. "The big blue sea" vs. "The letter C."
- high, hi: "A high mountain" vs. "Say hi to your friend."
- wear, where: "What will you wear?" vs. "Where are you going?"
- hare, hair: "A speedy hare" vs. "Long hair."
- air, heir: "Breathe fresh air" vs. "The heir to the throne."
- whether, weather: "I don't know whether to go" vs. "The weather is sunny."
- too, to, two: "Me too!" vs. "Go to the store" vs. "The number two."
- ate, eight: "I ate dinner" vs. "The number eight."
- no, know: "No, thank you" vs. "I know the answer."
- by, buy, bye: "Stand by me" vs. "Buy some candy" vs. "Say bye."
- flour, flower: "Bake with flour" vs. "A beautiful flower."
- right, write: "Turn right" vs. "Write a letter."
- be, bee: "To be happy" vs. "A buzzing bee."
- week, weak: "Seven days in a week" vs. "Feeling weak."
- rains, reins: "It rains a lot" vs. "Hold the horse's reins."
- higher, hire: "Go higher up" vs. "Hire a new employee."
- fare, fair: "Bus fare" vs. "A fair game."
Why are Homophones Important?
Understanding homophones is very important for clear communication, especially in writing. If you use the wrong homophone, your sentence might become confusing or even mean something completely different!
For example, if you write "I sea you" instead of "I see you," it changes the meaning from seeing with your eyes to seeing the ocean. Knowing the correct spelling helps you express your ideas accurately.
Homophones in Everyday Life
Homophones are everywhere! You'll find them in books, songs, movies, and conversations. Learning them helps you:
- Improve your spelling: You'll know which version of a word to use.
- Read better: You'll understand the intended meaning of words in context.
- Write clearly: Your messages will be easy for others to understand.
Many people, even adults, sometimes mix up homophones. It's a common challenge in English, but with practice, you can master them!
Related Words
Homophones are part of a larger group of words that sound or look similar.
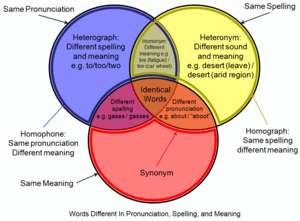
- Homonym: This is a broader term. Homonyms are words that are spelled the same and sound the same but have different meanings. For example, "bat" (a flying animal) and "bat" (a piece of sports equipment). Homophones are a type of homonym.
- Homograph: These are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings and sometimes different pronunciations. For example, "read" (present tense) and "read" (past tense).
Understanding these different word types helps you become a better reader and writer.
See also


