Human cloning facts for kids
Human cloning is when scientists make an exact copy of a human being, or even just human cells or tissues, from another human. It's like making a perfect duplicate!
There are two main kinds of human cloning:
- Therapeutic cloning: This is about making copies of cells or tissues for medical reasons. Scientists use it to study diseases or grow new body parts.
- Reproductive cloning: This type aims to create a complete human baby that is an exact copy of another person. This is very controversial and is not allowed in most places.
Contents
What is Human Cloning?
Human cloning means creating a copy of a human. This copy can be a whole person, or just specific parts like cells or tissues. The idea is to make something genetically identical to an existing human. Think of it like making a twin, but at a different time.
How Does Cloning Work?
The most common way scientists talk about cloning is called Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT). It sounds complicated, but here's the simple idea:
- Scientists take a normal body cell (like a skin cell) from the person they want to clone. This cell has all the DNA.
- Then, they take an egg cell from another person. They remove the DNA from this egg cell.
- Next, they put the DNA from the body cell into the empty egg cell.
- This new egg cell, with the new DNA, is given a small electric shock. This makes it start dividing and growing, just like a normal fertilized egg.
- If this growing cell mass is placed into a womb, it could develop into a complete organism.
Types of Human Cloning
Cloning isn't just one thing; it has different goals.
Therapeutic Cloning
Therapeutic cloning is used for medical research and treatments.
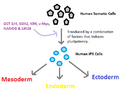
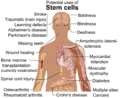
- Purpose: The main goal is to create stem cells. These are special cells that can turn into almost any other type of cell in the body.
- How it helps: Scientists hope to use these stem cells to grow new tissues or organs. For example, they might grow new heart cells for someone with heart disease, or new nerve cells for someone with a spinal cord injury.
- No new person: In therapeutic cloning, the cloned cells are never put into a womb to grow into a baby. They are only used in a lab for research or to create specific tissues.
Reproductive Cloning
Reproductive cloning aims to create a whole new human being that is genetically identical to another person.
- Purpose: To make a full copy of an existing human.
- Current status: No human has ever been successfully cloned this way. Scientists around the world generally agree that reproductive cloning of humans is unethical and dangerous.
- Why it's controversial: There are many ethical concerns. People worry about the safety of the cloned individual, their identity, and the impact on society.
Ethical Considerations
Human cloning brings up many important questions about right and wrong.
- Safety: Reproductive cloning is very risky. Animal cloning often results in health problems for the cloned animal.
- Identity: Some people worry about the unique identity of a cloned person. Would they be seen as a copy instead of an individual?
- Human dignity: Many believe that creating humans for specific purposes, like cloning, goes against human dignity.
- Laws: Because of these concerns, many countries have laws that ban human reproductive cloning.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Clonación humana para niños
In Spanish: Clonación humana para niños