Image: Comparison of skull features of Homo naledi and other early human species
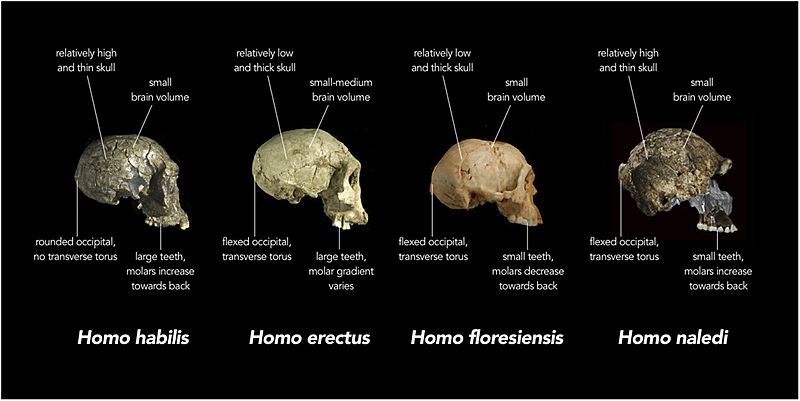
Description: Replica crania of (left to right) Homo habilis (KNM-ER 1813, Koobi Fora, Kenya ∼1.8 million years old), an early Homo erectus (D2700, Dmanisi, Georgia ∼1.8 million years old) and Homo floresiensis (Liang Bua 1, Indonesia ∼20,000 years old) are compared with actual fragments of cranial material of Homo naledi that have been overlaid on a virtual reconstruction (far right; note some of the images of H. naledi material have been reversed). In each case, the crania are labelled with the typical features of each species. For example, while the adult brain volume of modern humans (Homo sapiens) is typically between 1000 and 1500 cubic centimetres (cc), H. habilis ranged from about 510 to >700 cc, H. erectus from about 550 to >1100 cc, H. floresiensis about 426 cc, and H. naledi between 466 and 560 cc. Furthermore, in modern humans, the occipital bone (at the back of the skull) is typically evenly rounded in profile, whereas in some early humans such as H. erectus, the upper and lower portions of the occipital are sharply angled to each other (i.e., ‘flexed’), and there is a strong ridge of bone running across the angulated region (called a transverse torus).
Title: Comparison of skull features of Homo naledi and other early human species
Credit: Stringer, Chris (10s date QS:P,+10-00-00T00:00:00Z/8eptember 2015). "The many mysteries of Homo naledi". eLife 4: e10627. DOI:10.7554/eLife.10627. PMC: 4559885. ISSN 2050-084X.
Author: Chris Stringer, Natural History Museum, United Kingdom
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
License: CC BY 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following 2 pages link to this image:

