Immersion (mathematics) facts for kids
An immersion in mathematics is a special kind of function. It maps one shape or space into another. Think of it like drawing a line on a piece of paper. If you draw it smoothly without any sharp corners or places where it suddenly folds over itself, that's like an immersion.
In more complex math, an immersion takes a "manifold" (a space that looks flat when you zoom in, like the surface of a ball) and places it into another manifold. The key idea is that the immersion doesn't "pinch" or "fold" the original shape in a way that makes it lose its smoothness locally.
Contents
What is an Immersion?
An immersion is a way to put one shape inside another. Imagine you have a rubber band (a 1D circle). You can stretch it and place it on a table (a 2D flat space). If you do this without breaking the rubber band or making it cross itself at a sharp angle, that's an immersion.
Smoothness and Local Behavior
The most important part of an immersion is its "smoothness." This means that at every point, the shape doesn't have any sharp corners or sudden changes. It's like a smooth road without any potholes or sudden cliffs.
When we talk about "local behavior," we mean what happens very close to any single point on the shape. For an immersion, if you zoom in very, very close to any point, the shape looks flat and doesn't cross itself.
How Immersions are Different
Immersions are similar to, but different from, "embeddings." An embedding is an immersion that also doesn't cross itself anywhere, even if you look at the whole shape.
- An immersion can cross itself, but only in a smooth way. Think of a figure-eight shape. It crosses itself, but it's still smooth.
- An embedding never crosses itself at all. A simple circle drawn on paper is an embedding.
Examples of Immersions
Many interesting shapes in mathematics are immersions. They help us understand how different spaces can fit inside each other.
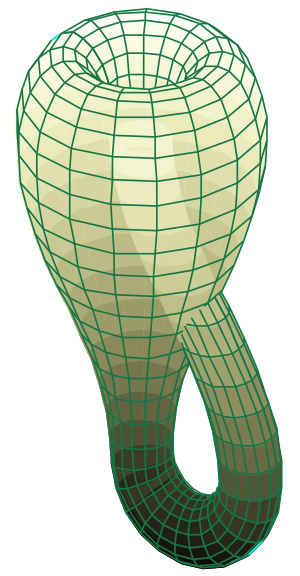
The Klein Bottle
The Klein bottle is a famous example of an immersion. It's a shape that has no inside or outside. If you try to build a Klein bottle in our normal three-dimensional space, it has to pass through itself. However, it does this in a smooth way, so it's an immersion.
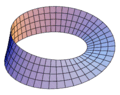
The Möbius Strip
The Möbius strip is another cool example. It's a surface with only one side and one edge. You can make one by taking a strip of paper, giving one end a half-twist, and then joining the ends. The Möbius strip can be smoothly immersed in 3D space without crossing itself.
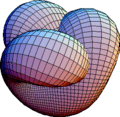
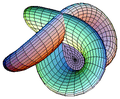
Boy's Surface and Morin Surface
Boy's surface and the Morin surface are other examples of immersions. These are ways to smoothly turn a sphere inside out without tearing or creasing it. They show how complex shapes can be smoothly placed into our everyday 3D space, even if they have to pass through themselves.
Why are Immersions Important?
Immersions are important in many areas of mathematics and physics. They help scientists and mathematicians understand:
- How different shapes can be related to each other.
- The properties of spaces that are hard to imagine directly.
- How to model complex systems, like the bending of light or the flow of fluids.
They are a basic tool for studying the shapes and structures of the universe.
Images for kids
-
The Möbius strip does not immerse in codimension 0 because its tangent bundle is non-trivial.
See also
 In Spanish: Inmersión (matemáticas) para niños
In Spanish: Inmersión (matemáticas) para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |