Kinetics facts for kids
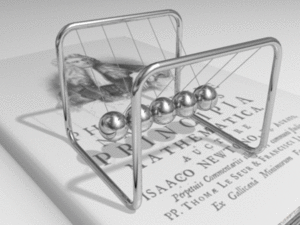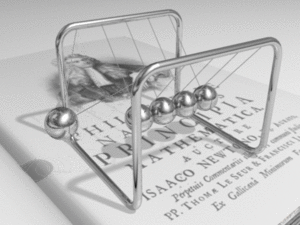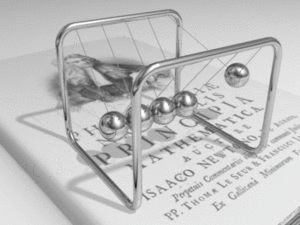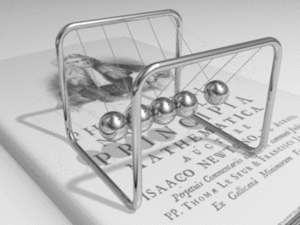
Kinetics is a part of physics that studies how things move and, more importantly, why they move. It looks at the forces that make objects start moving, speed up, slow down, or change direction.
Imagine a soccer ball. Kinetics helps us understand not just that the ball is moving, but also what made it move (like a kick) and how that kick affects its speed and path. It's all about figuring out the "agents" or causes behind motion.
Contents
What is Kinetics?
Kinetics is a key area within mechanics, which is the study of motion. While another part of mechanics, called kinematics, describes motion (like how fast something is going or how far it travels), kinetics goes deeper. It explores the reasons for that motion. This means looking at things like force, mass, and energy.
Force: The Cause of Motion
A force is a push or a pull. It's what makes an object change its state of motion. If an object is still, a force can make it move. If it's already moving, a force can make it speed up, slow down, or change direction. Kinetics helps us understand how different forces affect an object's movement.
For example, when you push a swing, you apply a force. Kinetics helps explain how strong that push needs to be to make the swing go higher or faster.
Mass and Acceleration
Two other important ideas in kinetics are mass and acceleration.
- Mass is how much "stuff" an object is made of. Objects with more mass are harder to get moving or to stop.
- Acceleration is how quickly an object's speed or direction changes.
Kinetics shows us the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. A larger force will cause a greater acceleration for a given mass. Also, a heavier object (one with more mass) will need a bigger force to accelerate at the same rate as a lighter object.
Newton's Laws and Kinetics
The ideas in kinetics are largely based on Isaac Newton's three laws of motion. These laws help us predict how objects will move when forces act on them.
- Newton's First Law (Law of Inertia): An object will stay still or keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line unless a force acts on it.
- Newton's Second Law (F=ma): The acceleration of an object depends on the force applied to it and its mass. This is often written as F = m × a (Force equals mass times acceleration). This law is central to kinetics.
- Newton's Third Law (Action-Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When you push on something, it pushes back on you with the same amount of force.
Kinetics uses these laws to solve problems and understand real-world situations, from how a car engine makes a car move to how a rocket launches into space.
Why is Kinetics Important?
Understanding kinetics is super important in many areas of life and science:
- Engineering: Engineers use kinetics to design safe cars, stable bridges, and powerful machines. They need to know how forces will affect structures and moving parts.
- Sports: Athletes and coaches use kinetics to improve performance. For example, understanding how a golfer swings a club or how a runner pushes off the ground involves kinetics.
- Space Exploration: When launching rockets or sending probes to other planets, scientists use kinetics to calculate the exact forces needed to get them where they need to go.
- Everyday Life: Even simple actions like riding a bike, throwing a ball, or walking involve the principles of kinetics.
Kinetics helps us make sense of the world around us and how everything moves.
See also
 In Spanish: Cinética para niños
In Spanish: Cinética para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |