Lidar facts for kids
Lidar is a cool technology that uses light to measure distances. It's like a super-smart flashlight that can tell you how far away things are. Lidar works by sending out tiny pulses of laser light. When these light pulses hit an object, they bounce back to a special sensor. By timing how long it takes for the light to return, Lidar can figure out the exact distance to the object. This technology is used in many exciting ways, from mapping the Earth to helping self-driving cars see the world around them.
Contents
How Lidar Works
Lidar stands for "Light Detection And Ranging." It uses a laser, which is a very focused beam of light. The Lidar system sends out many quick pulses of this laser light.
When a light pulse hits something, like a tree or a building, it reflects off that object. The reflected light then travels back to the Lidar sensor. The sensor measures how long it took for the light to leave and come back.
Since light travels at a known speed, the system can calculate the exact distance to the object. By sending out millions of pulses, Lidar can create a detailed 3D map of an area. This map is made of many tiny points, called a "point cloud."
The History of Lidar
Early Days of Lidar
The idea behind Lidar started soon after the laser was invented. In 1961, a company called Hughes Aircraft Company created one of the first tools like Lidar. It was first designed to track satellites orbiting Earth.
They called this new tool "Colidar." This name was a short way of saying "COherent Light Detecting And Ranging." It showed how the system used light to find and measure distances.
Lidar's First Uses
One of the first important uses for Lidar was in studying weather. Scientists at the National Center for Atmospheric Research began using it. They used Lidar to measure things like clouds and pollution in the air. This helped them understand our atmosphere better.
Over time, Lidar became more advanced. It started being used for many other things. These include mapping forests, helping robots move around, and guiding self-driving cars.
What Lidar Is Used For
Mapping and Surveying
Lidar is great for making very accurate maps. It can map large areas of land from airplanes or drones. It can even map the seafloor from special aircraft. This helps scientists understand the shape of the Earth. It also helps them find ancient ruins hidden under trees.
Self-Driving Cars
Many self-driving cars use Lidar to "see" their surroundings. The Lidar sensors on the car send out laser beams. These beams bounce off other cars, people, and obstacles. This creates a real-time 3D map of the road. This map helps the car know where it is and how to avoid crashes.
Robotics and Agriculture
Robots also use Lidar to navigate. A robot with Lidar can build a map of its environment. This helps it move around without bumping into things. In farming, Lidar can measure how much crops are growing. This helps farmers know where to water or fertilize their fields.
Everyday Devices
You might even have Lidar in your own home! Some newer smartphones and tablets have small Lidar scanners. These scanners help the device understand depth. This can improve photos, especially in low light. It also makes augmented reality (AR) apps work better.
Images for kids
-
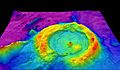
Lidar-derived image of Marching Bears Mound Group, Effigy Mounds National Monument
-
A frequency addition source of optical radiation (FASOR) used at the Starfire Optical Range for lidar and laser guide star experiments is tuned to the sodium D2a line and used to excite sodium atoms in the upper atmosphere.
-
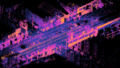
Lidar scanning performed with a multicopter UAV
-
This TomTom mapping van is fitted with five lidar sensors on its roof rack.
See Also
 In Spanish: LiDAR para niños
In Spanish: LiDAR para niños