Linear system facts for kids
In mathematics and systems theory, a linear system is a special kind of system. It works in a very predictable way. Imagine a machine where if you double the input, the output also doubles. That's a simple idea behind a linear system.
Most things in the real world are not perfectly linear. They are called non-linear systems. But understanding linear systems helps us understand more complex things.
Contents
What is a Linear System?
A linear system is like a simple rule machine. When you put something in, it gives you something out. The key is that its output is always directly related to its input. This relationship is often like a straight line on a graph.
Think of a simple light switch. If you flip it on, the light goes on. If you flip it off, the light goes off. This is a very basic system. A linear system has a more specific kind of predictable behavior.
How Do Linear Systems Work?
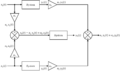
Linear systems follow two main rules. These rules make them very special and easy to predict. They are called additivity and homogeneity. When a system follows both, it obeys the superposition principle.
Adding Things Up (Additivity)
This rule means that if you combine two inputs, the output will be the sum of what you would get from each input alone.
Imagine you have a system that takes numbers.
- If you put in 2, it gives you 4.
- If you put in 3, it gives you 6.
For an additive system, if you put in 2 + 3 (which is 5), the output must be 4 + 6 (which is 10). It's like adding up the effects of each input separately.
Scaling Things (Homogeneity)
This rule means that if you multiply your input by a number, the output also gets multiplied by that same number.
Let's use our number system again:
- If you put in 2, it gives you 4.
For a homogeneous system, if you multiply the input 2 by 5 (making it 10), the output must be 4 multiplied by 5 (making it 20). The system scales the output in the same way it scales the input.
The Superpower of Superposition
The superposition principle is the big rule for linear systems. It combines both additivity and homogeneity. It means that if you have several inputs, you can figure out the total output by:
- Multiplying each input by a number.
- Finding the output for each of those new inputs.
- Adding all those individual outputs together.
This principle makes it much easier to analyze and design systems. Engineers and scientists use this idea all the time. It helps them predict how complex systems will behave.
Where Do We See Linear Systems?
While many real-world systems are non-linear, linear models are very useful. We often use them as simplified versions of more complex systems. This helps us understand them better.
Here are some places where linear systems are important:
- Electronics: Simple circuits with resistors, capacitors, and inductors can often be modeled as linear systems. This helps engineers design radios and computers.
- Control Systems: When you set the cruise control in a car, it uses a control system. Many of these systems are designed using linear principles. This helps keep your car at a steady speed.
- Signal Processing: When your phone processes sound or images, it often uses linear filters. These filters help clean up noise or change the sound.
- Physics: Many basic laws of physics, like Hooke's Law for springs, describe linear relationships. If you pull a spring twice as hard, it stretches twice as much.
Understanding linear systems is a key step in learning about how many technologies and natural processes work.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sistema lineal para niños
In Spanish: Sistema lineal para niños