Magnetic pole facts for kids
Magnetic poles are special places on Earth where its invisible magnetic force, called the magnetic field, points straight up or down. Think of Earth as a giant magnet! The magnetic field is what makes a compass needle point north. These magnetic poles are always moving, and they are not exactly in the same spot as the geographic North and South Poles that you see on maps.
Contents
What Are Magnetic Poles?
Earth has a powerful magnetic field that surrounds it, stretching far into space. This field is created by the movement of hot, liquid iron deep inside Earth's core. Just like a bar magnet has a north and south pole, Earth's magnetic field also has two main poles: the North Magnetic Pole and the South Magnetic Pole.
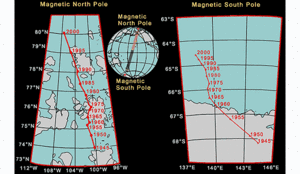
North Magnetic Pole
The North Magnetic Pole is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where Earth's magnetic field lines point straight downwards. This is the spot that a compass needle tries to point towards. However, it's important to remember that the North Magnetic Pole is not the same as the geographic North Pole, which is the top point of Earth's axis of rotation.
South Magnetic Pole
Similarly, the South Magnetic Pole is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the magnetic field lines point straight upwards. Just like its northern counterpart, it is not located at the geographic South Pole.
Why Do Magnetic Poles Move?
The magnetic poles are not fixed in one place. They are always slowly drifting across Earth's surface. This movement happens because the liquid iron in Earth's outer core is constantly flowing and swirling. These movements create electric currents, which in turn generate Earth's magnetic field. Since the flow of this liquid iron changes over time, the magnetic field and its poles also change their position.
How Fast Do They Move?
Scientists have been tracking the magnetic poles for many years. The North Magnetic Pole, for example, has been moving quite quickly in recent decades. It has shifted from northern Canada towards Siberia. Sometimes it moves a few kilometers a year, and other times it can move much faster, even up to 50 or 60 kilometers (about 30 to 37 miles) in a single year!
Importance of Magnetic Poles
Earth's magnetic field and its poles are very important for life on our planet.
- Navigation: For centuries, explorers and travelers have used compasses to find their way. Compasses work by aligning with Earth's magnetic field, pointing towards the magnetic poles. Even today, ships and planes use magnetic compasses as a backup to modern GPS systems.
- Animal Migration: Many animals, like birds, sea turtles, and salmon, use Earth's magnetic field to help them navigate during their long migrations. They have a special sense that allows them to detect the magnetic field and use it like an internal map.
- Protecting Earth: The magnetic field acts like a shield, protecting Earth from harmful radiation and charged particles from the Sun, known as solar wind. Without this magnetic shield, our atmosphere could be stripped away, making life on Earth very difficult.
Magnetic Reversals
Scientists have discovered that Earth's magnetic poles have completely flipped many times throughout history. This means the North Magnetic Pole becomes the South Magnetic Pole, and vice versa. These events are called magnetic reversals. They don't happen suddenly; it's a slow process that takes thousands of years. The last full reversal happened about 780,000 years ago. While a reversal might cause some temporary changes, like compasses pointing south instead of north, it's a natural part of Earth's geological history.
See also
In Spanish: Polo magnético para niños