Memory facts for kids
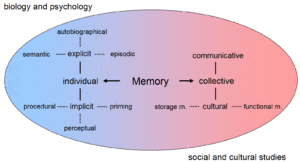
Memory is your brain's amazing ability to store and recall information. It's like your personal record of everything you've seen, heard, felt, and learned! Scientists who study how our brains work, especially how we think and remember, call this field "cognitive psychology".
There are three main types of memory that help us remember different things for different lengths of time:
- Short-term memory: This holds information for a very brief time, like a phone number you're about to dial.
- Sensory memory: This is super-quick memory. It captures what your senses notice for a split second.
- Long-term memory: This is where you store information for a long time, even your whole life.
Sometimes, people experience memory loss. This is often called forgetfulness or amnesia.
Contents
What is Sensory Memory?
Sensory memory is the very first, super-fast stage of memory. It holds sensory information (what you see, hear, or feel) for less than a second. Think of it like a quick snapshot of your senses. It happens automatically!
For example, if you quickly glance at a picture, your sensory memory holds that image for a tiny moment. A scientist named George Sperling did famous experiments in 1963. He showed that our sensory memory can hold about 12 items. But they disappear very, very quickly – within a few hundred milliseconds! You can't really practice to keep sensory memories longer.
There are three main kinds of sensory memory:
- Iconic memory: This is for visual information, like a quick flash of an image.
- Echoic memory: This is for sounds, like briefly remembering the last few words someone said.
- Haptic memory: This is for touch sensations.
What is Short-Term Memory?
Short-term memory is also known as working memory. This is because your brain actively holds and works with information here. It allows you to remember things for a few seconds up to about a minute. This is without repeating them over and over.
However, its capacity is quite limited. A famous researcher named George Armitage Miller (1956) found that most people can only hold about 7 items at once. More recent studies suggest it might be even less, around 4 or 5 items.
How Can You Remember More in Short-Term Memory?
You can remember more in short-term memory using a trick called chunking. This means grouping individual pieces of information into larger, more meaningful "chunks."
For example, a ten-digit phone number like 1234567890 is easier to remember. You can remember it as three chunks: 123-456-7890. Your brain sees three chunks instead of ten separate digits. This makes it easier to hold in your short-term memory. This is why phone numbers are often displayed in groups!
Short-term memory mostly relies on how things sound (an acoustic code). It stores information less on how they look. For instance, if you hear a list of letters, you're more likely to mix up letters that sound similar (like E and P).
What is Long-Term Memory?
Unlike sensory and short-term memory, long-term memory can store a huge amount of information. It can store it for a very long time – potentially your entire life! Its capacity is practically endless. For example, you might remember a new phone number for only a few seconds. But you can remember your home phone number for many years. This is because it's stored in your long-term memory.
While short-term memory often uses sound to remember things, long-term memory tends to store information based on its meaning. This is called a semantic code. So, if you're trying to remember a list of words, you're more likely to mix up words that have similar meanings (like "big," "large," "huge").
Types of Long-Term Memory
One important part of long-term memory is episodic memory. This is your memory for specific events that happened to you. It includes "what" happened, "when" it happened, and "where" it happened. Episodic memory lets you recall personal experiences. These could be your last birthday party or a family vacation.
How Does the Brain Store Long-Term Memories?
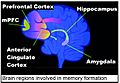
Short-term memories are held by temporary patterns of brain activity. This happens especially in the front and side parts of your brain. Long-term memories, however, involve more lasting changes in the connections between brain cells. These changes are spread out across many parts of the brain.
The hippocampus, a small part of your brain shaped like a seahorse, is super important. It helps turn new information from short-term into long-term memory. It doesn't actually store the memories itself. But it acts like a temporary processing center. Scientists learned a lot about the hippocampus from a famous patient named Henry Molaison. He couldn't form new long-term memories after parts of his hippocampus were removed.
Understanding the Multi-Store Model of Memory
In 1968, two scientists, Atkinson and Shiffrin, came up with a way to explain how memory works. It's called the multi-store model. This model suggests that memory flows through three main stages:
- Information first enters your sensory memory.
- If you pay attention to it, it moves into your short-term memory.
- If you practice or repeat the information (this is called rehearsal), it can then be transferred into your long-term memory.
However, this model has been criticized for being a bit too simple. For example, we now know that long-term memory isn't just one big storage unit. It has different parts, like episodic memory (for events) and procedural memory (for skills, like riding a bike). Also, we can sometimes remember things without constantly repeating them. The model didn't fully explain this.
Research has also shown that short-term memory isn't just one single unit. For instance, a patient named 'KF' had brain damage. This affected his ability to remember sounds (like spoken numbers) in his short-term memory. But his visual short-term memory was fine. This suggests that our short-term memory might have separate parts for visual and auditory information.
Exploring the Working Memory Model
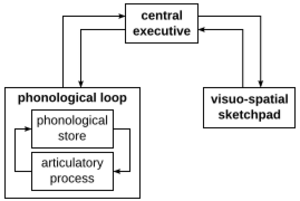
Because the multi-store model was a bit too simple for short-term memory, two other scientists, Baddeley and Hitch, proposed the working memory model in 1974. This model describes short-term memory as an active workspace. Here, we not only store information temporarily but also actively process and manipulate it.
The working memory model has three main parts, plus one added later:
- The Central Executive: This is like the boss of working memory. It controls your attention. It decides which information to focus on and send to the other parts of working memory.
- The Phonological Loop: This part deals with auditory (sound) information. It's like an inner voice that silently repeats sounds or words. This helps you remember them, like when you repeat a phone number to yourself.
- The Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad: This part handles visual and spatial information. It's what you use when you're trying to imagine how many windows are on your house or figuring out directions.
- The Episodic Buffer: (Added in 2000) This part connects information from the other working memory components. It links it with your long-term memory. It helps you create a complete picture of an experience, like remembering a story or a movie scene in order.
This working memory model helps explain why it's easier to do two different tasks at once (like listening to music and drawing). It's harder to do two similar tasks (like reading and listening to a podcast). Working memory is essential for our everyday thinking, learning, and problem-solving.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Memoria (proceso) para niños
In Spanish: Memoria (proceso) para niños
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |