Molecular cloning facts for kids
Molecular cloning is a cool technique used in molecular biology. It's like building with DNA! Scientists use it to put together new DNA molecules, called recombinant DNA. Then, they make copies of this new DNA inside living things, called host organisms.
When we say "cloning" here, it means taking a DNA molecule from one cell and making many, many copies of it. All these copies are exactly the same. Molecular cloning is super important for many things in modern biology and medicine.
This process often uses DNA from two different places. First, there's the DNA you want to copy. Second, there's a living host, usually a tiny germ, that will help make lots of copies of your new DNA.
Contents
What is Recombinant DNA?
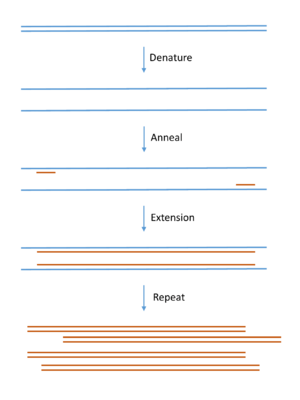
In a molecular cloning experiment, scientists first get the DNA they want to study or use. They take it from an organism, like a plant or an animal. Then, they use special tools, like enzymes, to cut this DNA into smaller pieces.
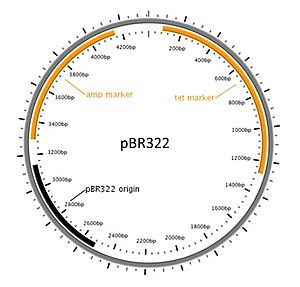
These small DNA pieces are then joined with another type of DNA called vector DNA. Think of vector DNA as a delivery truck for the new DNA. When the pieces are joined, they form a recombinant DNA molecule. It's "recombinant" because it combines DNA from different sources.
How Does Cloning Work?
After making the recombinant DNA, scientists put it into a host organism. Often, they use a common type of bacteria called E. coli. These bacteria are easy to grow in the lab and are usually harmless.
Once inside the bacteria, the recombinant DNA gets copied along with the bacteria's own DNA. This creates a whole group of bacteria that all have copies of the new DNA. Because these bacteria now have DNA from another source, they are called "transgenic" or "genetically-modified microorganisms" (GMOs).
It's amazing because just one bacterial cell can take in one recombinant DNA molecule. Then, that single cell can multiply very quickly. This makes a huge number of bacteria, and each one has copies of the original recombinant DNA. So, both the group of bacteria and the new DNA molecule are often called "clones."
Who Invented Molecular Cloning?
The idea of using molecular cloning to create recombinant DNA came from a scientist named Paul Berg. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1980 for his work. He shared the prize with Walter Gilbert and Fred Sanger.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Clonación de genes para niños
In Spanish: Clonación de genes para niños