Morphology (biology) facts for kids
Morphology is the study of the shape and structure of living things. It looks at what an animal or plant looks like, both on the outside and the inside. Think of it as studying the "blueprint" of a living organism.
The idea of morphology was first developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe in 1790. Another German scientist, Karl Friedrich Burdach, also worked on this idea around 1800.
In simple terms, morphology describes the overall form and structure of an organism. This includes its outer appearance, like its shape, color, and patterns. It also covers the structure of internal parts, such as bones and organs. Morphology is different from physiology, which is the study of how these parts work or function.
Contents
What is Morphology?
Morphology helps us understand why living things look the way they do. It explores how different parts of an organism are put together. For example, why does a bird have wings, or why does a fish have fins? Morphology helps answer these questions by looking at their structure.
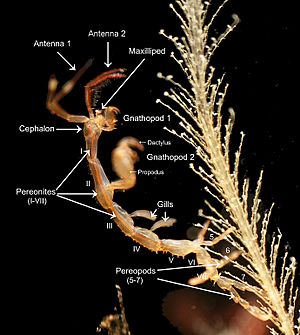
External and Internal Features
- External features are what you can see on the outside. This includes the shape of an animal's body, the number of its limbs, or the color of a flower.
- Internal features are what's inside. This means studying bones, muscles, and organs like the heart or lungs.
Types of Morphology
Scientists study morphology in different ways to learn more about living things.
Comparative Morphology
Comparative morphology looks at how the body structures of different organisms are similar or different. For example, comparing the bones in a human arm to those in a bat's wing shows how they are alike, even though they are used for different things. This helps us understand how species are related.
Functional Morphology
Functional morphology explores the connection between a structure and its job. It asks: "How does this part's shape help it do its work?" For instance, the strong, sharp teeth of a lion are perfectly shaped for tearing meat. This type of morphology helps us understand how animals survive in their environments.
Experimental Morphology
Experimental morphology studies how outside factors can change an organism's shape. Scientists might do experiments to see how things like genetic changes or environmental conditions affect an animal's development. This helps us learn about growth and how bodies adapt.
Anatomy
Anatomy is a part of morphology that focuses specifically on the internal structures of an organism. When you study anatomy, you learn about the bones, organs, and tissues inside a body. It's like looking at the inner workings of a complex machine.
See also
 In Spanish: Morfología (biología) para niños
In Spanish: Morfología (biología) para niños