Anatomy facts for kids
Anatomy is the study of the bodies of people and animals. It looks at both the inside and outside of the body. When you study anatomy, you learn about where organs like muscles, glands, and bones are located. You also learn how they are built. A person who studies anatomy is called an anatomist.
Contents
A Look Back: The History of Anatomy
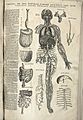
People have been studying anatomy for a very long time. The ancient Egyptians started studying human anatomy around 1600 BC. They learned what many organs like the liver, spleen, kidneys, and heart do. They were also the first to discover how the lymphatic system works.
For many years, it was not allowed to study human bodies closely. This made it hard to learn correct information about how our bodies are put together.
What Anatomists Do
Human anatomists often work at universities, medical schools, or hospitals. They usually teach students and do research.
There are two main types of anatomy:
- Gross anatomy studies parts of the body that are big enough to see with your eyes. This includes organs, bones, and muscles.
- Micro-anatomy studies smaller parts of the body. You need a microscope to see these tiny structures.
Anatomy is one of the basic sciences used in medicine. Other similar sciences include physiology (how the body works) and biochemistry (the chemistry of living things).
Exploring Body Systems
Our bodies are made up of different organ systems. Each system has a special job. Here are a few examples:
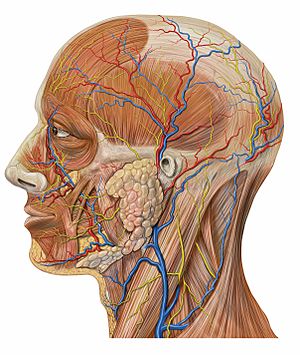
- The circulatory system moves blood all around your body. It includes your heart, blood, and blood vessels.
- The muscular system is made of all your muscles. These help you move, lift, and do many other actions.
- The nervous system controls your nerves and your brain. It helps you think, feel, and react to the world.
- The skeleton is made of all your bones. It gives your body shape and protects your organs.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
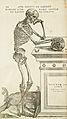
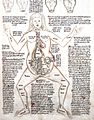
One of the large, detailed illustrations in Andreas Vesalius's De humani corporis fabrica 16th century, marking the rebirth of anatomy
-
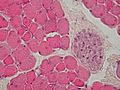
Cross section through skeletal muscle and a small nerve at high magnification (H&E stain)
-
Mouse skull
-
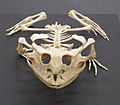
Skeleton of Surinam horned frog (Ceratophrys cornuta)
-
Skeleton of a diamondback rattlesnake
-
Part of a wing. Albrecht Dürer, c. 1500–1512
-
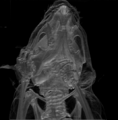
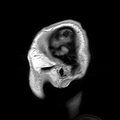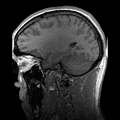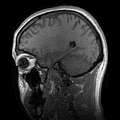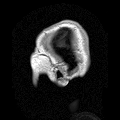
Modern anatomic technique showing sagittal sections of the head as seen by an MRI scan
-
Head of a male Daphnia, a planktonic crustacean
-
Surgical instruments were invented for the first time in history by Abulcasis in the 11th century
-
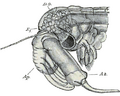
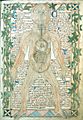
Anatomy of the eye for the first time in history by Hunayn ibn Ishaq in the 9th century
-
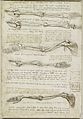
Anatomical study of the arm, by Leonardo da Vinci, (about 1510)
-
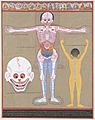
Anatomical chart in Vesalius's Epitome, 1543
See also
 In Spanish: Anatomía para niños
In Spanish: Anatomía para niños